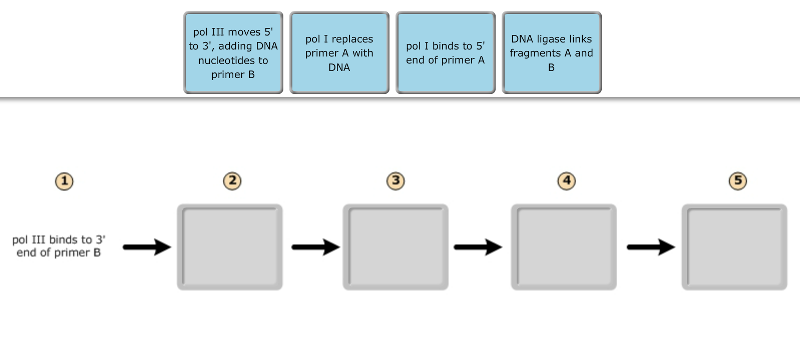
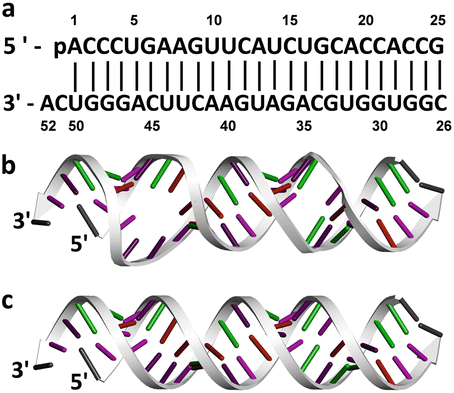
The nucleotides combine with each other to form a polynucleotide, DNA or RNA Each nucleotide is made up of three components a nitrogenous base, a pentose (fivecarbon) sugar, and a phosphate group (Figure 2) Each nitrogenous base in a nucleotide is attached to a sugar molecule, which is attached to a phosphate group2 A nucleotide is made of three parts a phosphate group, a five carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base Slide 9 3 In a single strand of DNA, the phosphate group binds to the sugar of the next nucleotide Slide 5 4In writing nucleotide sequences for nucleic acids, the convention is to write the nucleotides (usually using the oneletter abbreviations for the bases, shown in Figure 2814) starting with the nucleotide having a free phosphate group, which is known as the 5′ end, and indicate the nucleotides in order

Freight Operations Geodis
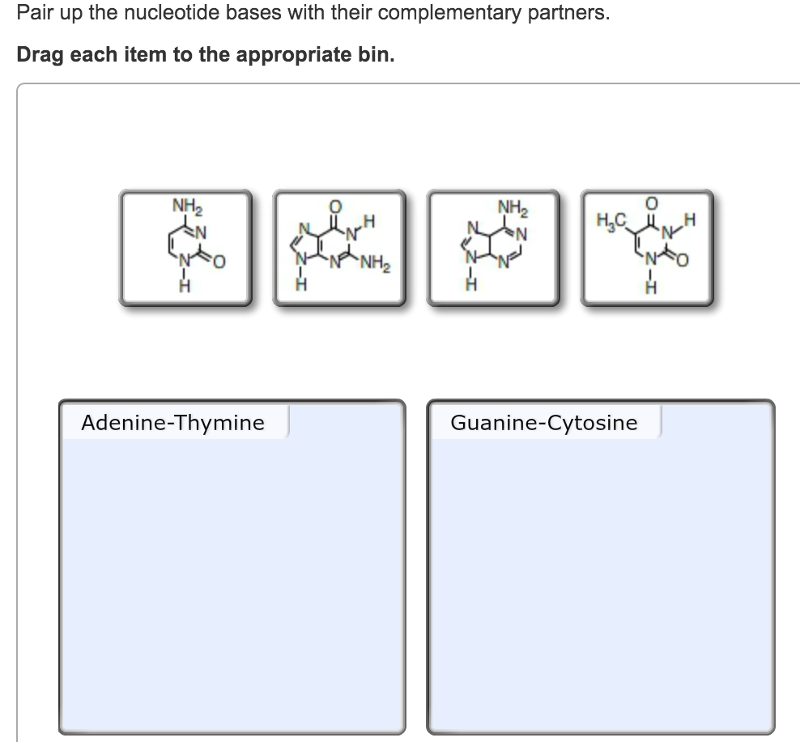
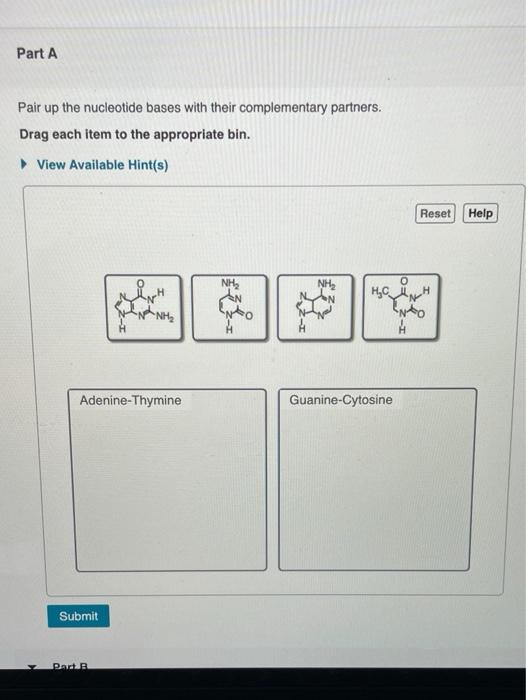
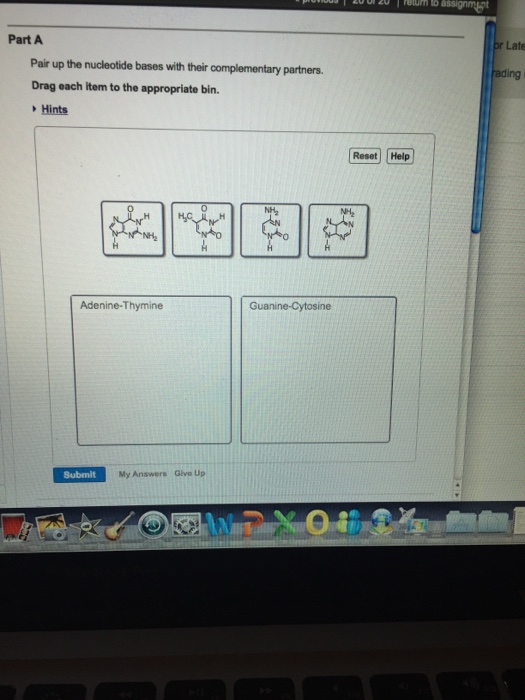
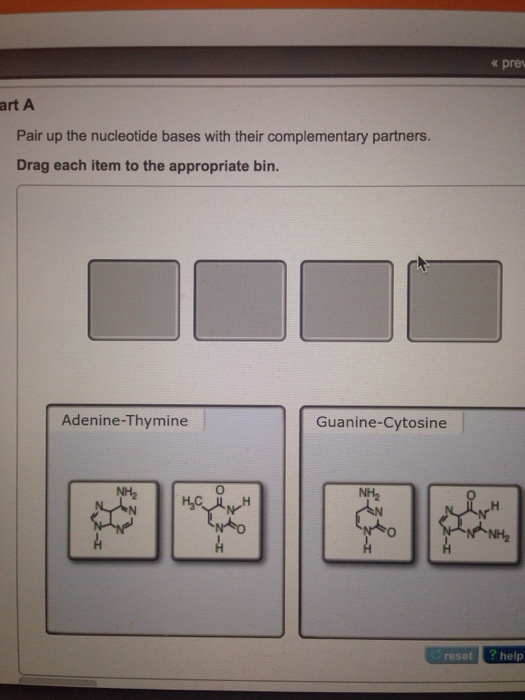
Pair up the nucleotide bases with their complementary partners.drag each item to the appropriate bin
Pair up the nucleotide bases with their complementary partners.drag each item to the appropriate bin-Q Pair up the nucleotide bases with their complementary partners Drag each Item to the appropriate bin Drag each Item to the appropriate bin Q Sort these nucleotide building blocks by their name or classificationEach base pair extends 034 nm For an interesting comparison, your body contains about 05 g of DNA!




Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Co Clutch Prep
Drag each item to the appropriate bin ANSWER Correct In a DNA sequence, the purine adenine always pairs with the pyrimidine thymine, and the purine guanine always pairs5 DNA Bending Assume that a poly(A) tract five base pairs long produces a bend of about ° Calculate the total (net) bend produced in the DNA if the center base pairs (the third of five) of two The phosphate is connected to the pentose sugar;
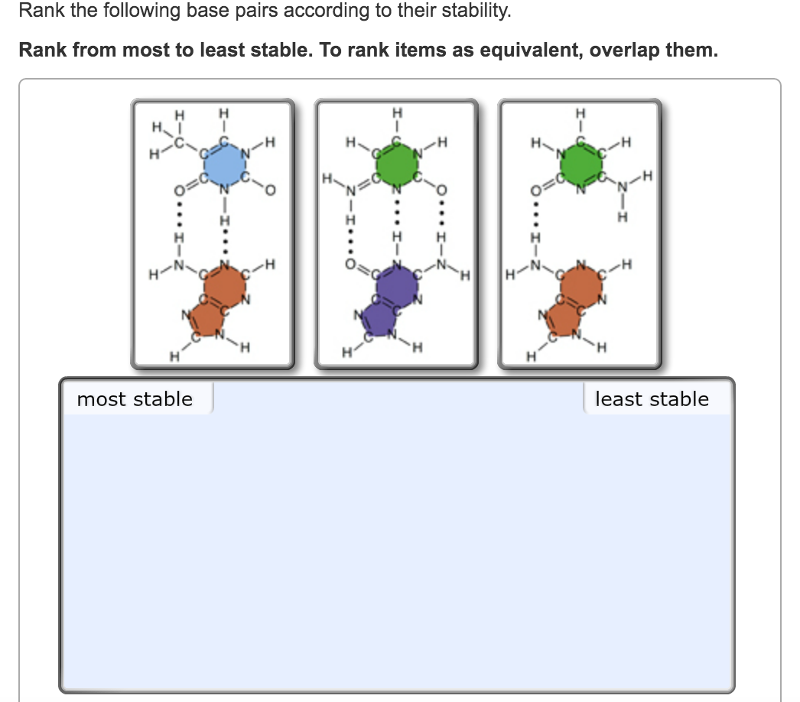
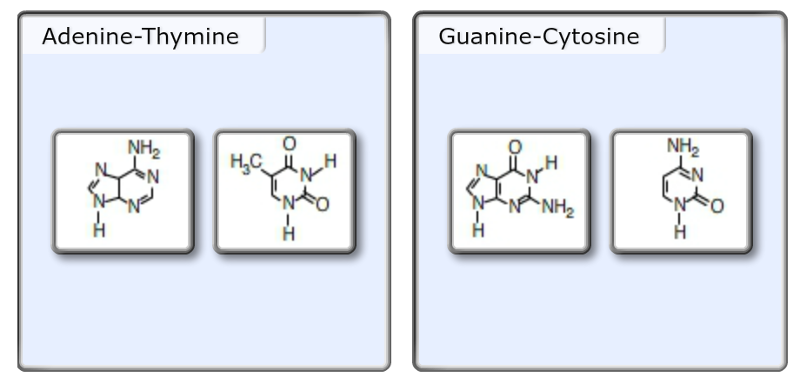
4 during which stage of the cell cycle do the chromosomes appear in the form of chromatin?Stable pairings occur between guanine and cytosine and between adenine and thymine (or adenine and uracil in RNA) Three hydrogen bonds form between guanine and cytosine Two hydrogen bonds form between adenine and thymine or adenine and uracil Complementary pairs always involve one purine and one pyrimidine base *A release factor (protein) will move into the A site instead of tRNA The release factor hydrolyzes the bond between the tRNA in the P site and the last amino acid of the polypeptide chain The polypeptide is then freed from the ribosome The 2 ribosomal subunits and other components dissociate A protein is made!
2 during which phase of the cell cycle is the nucleus divided? All these abilities depend on the pairing of complementary bases Figure 107 "Complementary Base Pairing" shows the two sets of base pairs and illustrates two things First, a pyrimidine is paired with a purine in each case, so that the long dimensions of both pairs are identical (108 nm) A nucleotide is an organic molecule made up of a sugar, a phosphate, and a nucleotide base It is the basic unit of DNA and RNA A nucleotide does not contain an amino acid




Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Co Clutch Prep




Usb2 Unit Selection Text To Speech Synthesis Based On Predicted Concatenation Parameters Google Patents
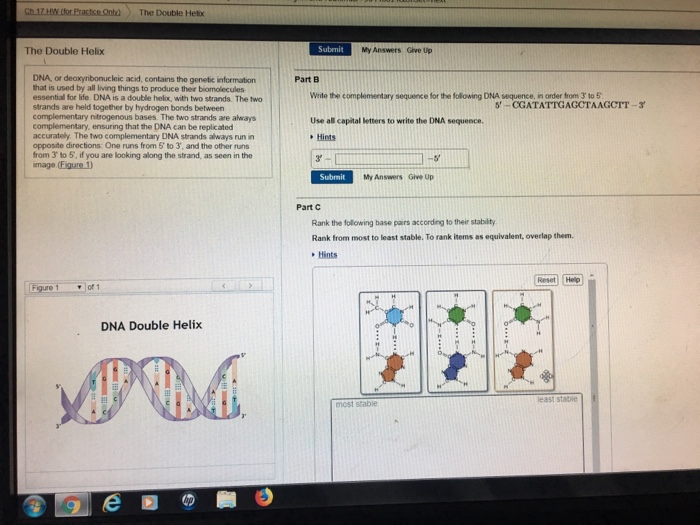
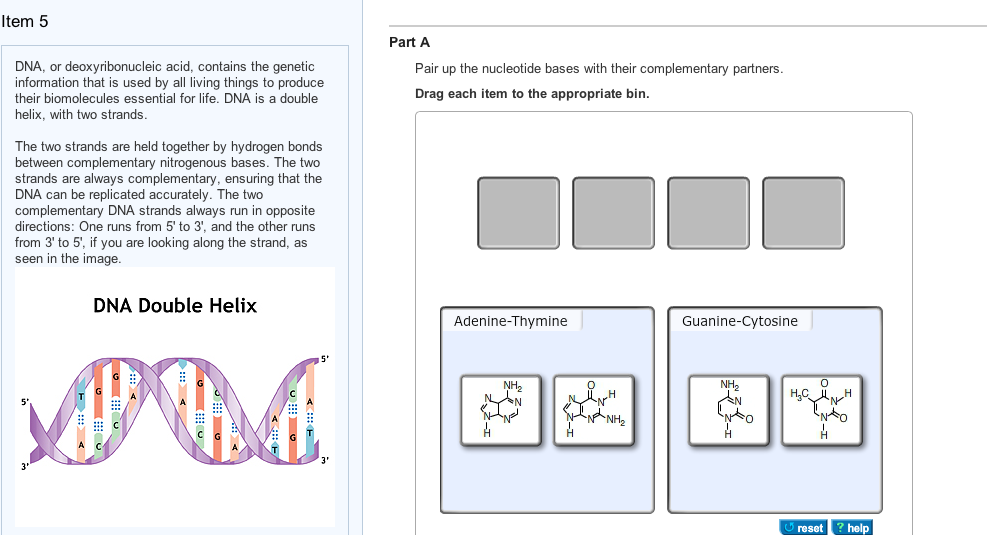
Enter only the nucleotides, and put your answer in the 5' to3 DNA is organized and arranged in the nucleus as?The two complementary DNA strands always run in opposite directions One runs from 5' to 3', and the other runs from 3' to 5', if you are looking along the strand, as seen in the image DNA Double Helix Part A Pair up the nucleotide bases with their complementary partners Drag each item to the appropriate bin



Print Exam 3 Chs 5 Dna Structure And Replication Machinery 16 The Molecular Basis Of Inheritance Flashcards Easy Notecards




Systemic Psychophysiology Handbook Of Psychophysiology
Watson and Crick proposed that the DNA is made up of two strands that are twisted around each other to form a righthanded helix, called a double helix Basepairing takes place between a purine and pyrimidine namely, A pairs with T, and G pairs with C In other words, adenine and thymine are complementary base pairs, and cytosine and guanine are also complementary base pairsThe two complementary DNA strands always run in opposite directions One runs from 5' to 3', and the other runs from 3' to 5', if you are looking along the strand, as seen in the image(Figure 1) Part A Part complete Pair up the nucleotide bases with their complementary partners Drag each item to the appropriate binA) half the basepairs will be AG pairs and half will be CT pairs b) each base will form at least two hydrogen bonds with a base in the opposite strand c) the two strands will form an antiparallel lefthanded helix with 12 base pairs per turn d) there will be covalent phosphodiester bonds between the two strands




Bsc 10 Ch 16 17 18 Review Flashcards Quizlet



Print Exam 3 Chs 5 Dna Structure And Replication Machinery 16 The Molecular Basis Of Inheritance Flashcards Easy Notecards
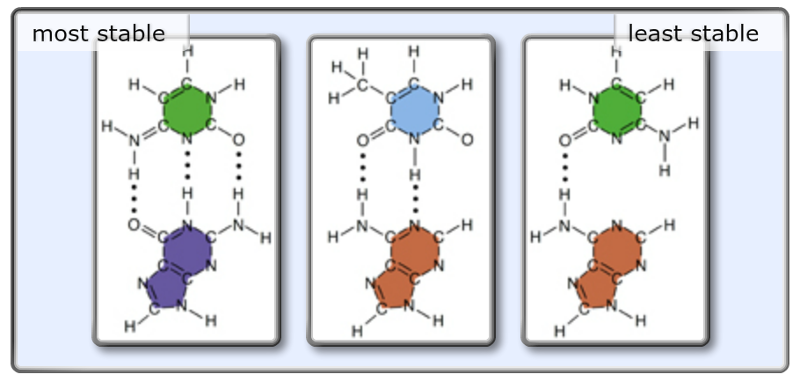
Protocol In a large cup, warm 150ml of water to 40˚C While that is warming, in a second cup create a 150ml ice bath Fill a third large cup with 150ml of room temperature water Cut your apple into six slices and assemble the following treatments Room temperature incubator Place apple slice in dry, small cup Hot incubator Rank the following base pairs according to their stability Rank from most to least stable To rank items as equivalent, overlap them I have found out that the first one is thymineadenine pair and the second one is a cytosineguanine pair The third one is cytosine paired with adenine, which doesn't make sense, so it must be the least stableEach strand is a polymer of DNA nucleotides Each nucleotide consists of a sugar, a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases The structure and orientation of the two strands are important to understanding DNA replication




Advances In Protein Chemistry



Problem Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Complementary Par
The pentose sugar is connected to the nitrogenous base pair (A, C, G or T), which in DNA is connected to its base pair partner Something like this Image Source Wikimedia Commons Figure 5 Nucleotide bonding in the DNA molecule with hydrogen and phosphate bondsA nucleotide is a compound, which can form a polynucleotide chain by the union of nitrogenous bases and sugarphosphate group Monomers of nucleotide units are connected via a covalent phosphodiester bond Nitrogenous bases, ie purines and pyrimidine, are attached via weak hydrogen bonds The bases link with a deoxyribose pentose sugar via anDue to DNA's doublehelical structure, the nucleotide bases are paired Adenine is paired with thymine and guanine is paired with cytosine Chargaff found that there is typically an equivalent number of adenine and thymine bases, and an equivalent number of guanine and cytosine bases




Latest Improvements For Qiagen Clc Genomics Workbench Archive Qiagen Bioinformatics



Www Bnl Gov Education Docs 17 Internship Report Pdf
Distinguish purines from pyrimidines Distinguish the purines from the pyrimidines Drag each item to the appropriate bin ANSWER Correct In a DNA sequence, the purine adenine always pairs with the pyrimidine thymine, and the purine guanine always pairs with the pyrimidine cytosine Part A – The chemical structure of DNA and its nucleotides The DNA double helix is composed of two strands of DNA; Levels of Protein Structure The structure of proteins is generally described as having four organizational levels The first of these is the primary structure, which is the number and sequence of amino acids in a protein's polypeptide chain or chains, beginning with the free amino group and maintained by the peptide bonds connecting each amino acid to the next



Live Updates Global Covid 19 Cases Top 92 Million



Www Hsdl Org View Did
What would be the complementary sequence of nucleotides for the following DNA sequence GCTAATTGCATCCGA?Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Complementary Partnersdrag Each Item To The Appropriate Bin Part A Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Complementary Partners Drag Each Course Hero Sequence Assembly And Mapping With Mira 5Part A Pair up the nucleotide bases with their complementary partners Drag each item to the appropriate bin Hint 1 The difference between purines and pyrimidines The complementary partners in a DNA base pair are always made up of one purine and one pyrimidine, never two purines or two pyrimidines Purines are the nucleotides that have the




Problem Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Complementary Par



Machines Secure Assigr The Double Helx The Double Chegg Com
How does the replication process ensure that new DNA molecule is identical to the original (that there are no mutations)?Critical Thinking Questions 7 Cellular Respiration Introduction 71 Energy in Living Systems 72 Glycolysis 73 Oxidation of Pyruvate and the Citric Acid Cycle 74 Oxidative Phosphorylation 75 Metabolism without Oxygen 76 Connections of Carbohydrate,Complementary nucleotide bases concept questions The following questions test understanding of concepts in the Complementary Nucleotide Bases interactive illustration There are 5 questions See how many you can get right View the illustration Related Content Illustrations Nucleotides in DNA Nucleotides in RNA




Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Co Clutch Prep



Shown In The Picture The Nucleotide Bases And Chegg Com
Pair up the nucleotide bases with their complementary partners Drag each Item to the appropriate bin 0324 PM SolutionpdfFor standard Mastering assignments and any Adaptive FollowUp assignments To complete an assignment — You need to complete ALL of its forcredit items, or all extra credit items if there are no forcredit items To get the most credit, check the grading policy before you work on an assignment Stop and restart an assignment — All of yourSpecific base pairing in DNA is the key to copying the DNA if you know the sequence of one strand, you can use base pairing rules to build the other strand Bases form pairs (base pairs) in a very specific way Figure 8 shows how A (adenine) pairs with T (thymine) and G (guanine) pairs with C (cytosine)




Roche Lightcycler 480 1536 Operators Manual Manualzz



Hydrogen Bonding In Dna Base Pairs
See Page 1 Part A Pair up the nucleotide bases with their complementary partners Drag each item to the appropriate bin You did not open hints for this part ANSWER 6/8/16 Mastering Assignment 2 (M2) 3/8 Part B Write the complementary sequence for the following DNA sequence, in order from 3' to 5' Use all capital letters to write the DNAA base pair is one of the pairs AT or CG Notice that each base pair consists of a purine and a pyrimidine The nucleotides in a base pair are complementary which means their shape allows them to bond together with hydrogen bonds The AT pair forms two hydrogen bonds The CG pair forms three4 18 g per 1,000 nucleotide pairs;



Reset Help Mrna Combines With Ribosome Amino Acids Chegg Com



Http Www Ncdsv Org Images Doj Dnaforthedefensebar 6 12 Pdf
Pair up the nucleotide bases with their complementary partners Drag each Item to the appropriate binPolar Side Chains Side chains which have various functional groups such as acids, amides, alcohols, and amines will impart a more polar character to the amino acid The ranking of polarity will depend on the relative ranking of polarity for various functional groups as determined in functional groupsIn addition, the number of carbonhydrogens in the alkane or aromatic portion Keyboard shortcuts Enter math expressions Updated You can use keyboard shortcuts to enter the following formats, Greek letters, symbols, and special functions for mathematical expressions, whether answering on a computer, tablet, or smartphone



2




This Week In Mac Sports 9 15 The Mac Weekly
If the length of the genome in base pairs is 6X 10 9/cell, the total length of the genome in ALL the cells in a human is = (5 X 1013) x (6X 109) bp If the size of each base pair is 034 nm, the total length of the genome in ALL the cells in a human is = (56 Which of the following best explains how complementary basepairing is involved in DNA replication?A chemical bond between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the sugar of a neighboring nucleotide holds the backbone together Chemical bonds (hydrogen bonds) between the bases that are across from one another hold the two strands of the double helix together Bases There are four types of bases in DNA They are called * Adenine (A) * Cytosine



Www Media Discoveryeducation Com Wp Content Uploads 05 Ca Stb High Biology Labs Pdf




February 22 3rd Section By Dairy Star Issuu
Question 6 SURVEY 60 seconds Q In a molecule of doublestranded DNA, the amount of Adenine present is always equal to the amount of answer choices cytosine guanine thymine1 during which phase of the cell cycle is DNA replicated? The complementary nucleotide sequence is thus the base pair with which it forms a doublestranded structue of the DNA, for example the complementary sequence for "ACGTTTA" is "TGCAAAT" Wiki User



Print Exam 3 Chs 5 Dna Structure And Replication Machinery 16 The Molecular Basis Of Inheritance Flashcards Easy Notecards
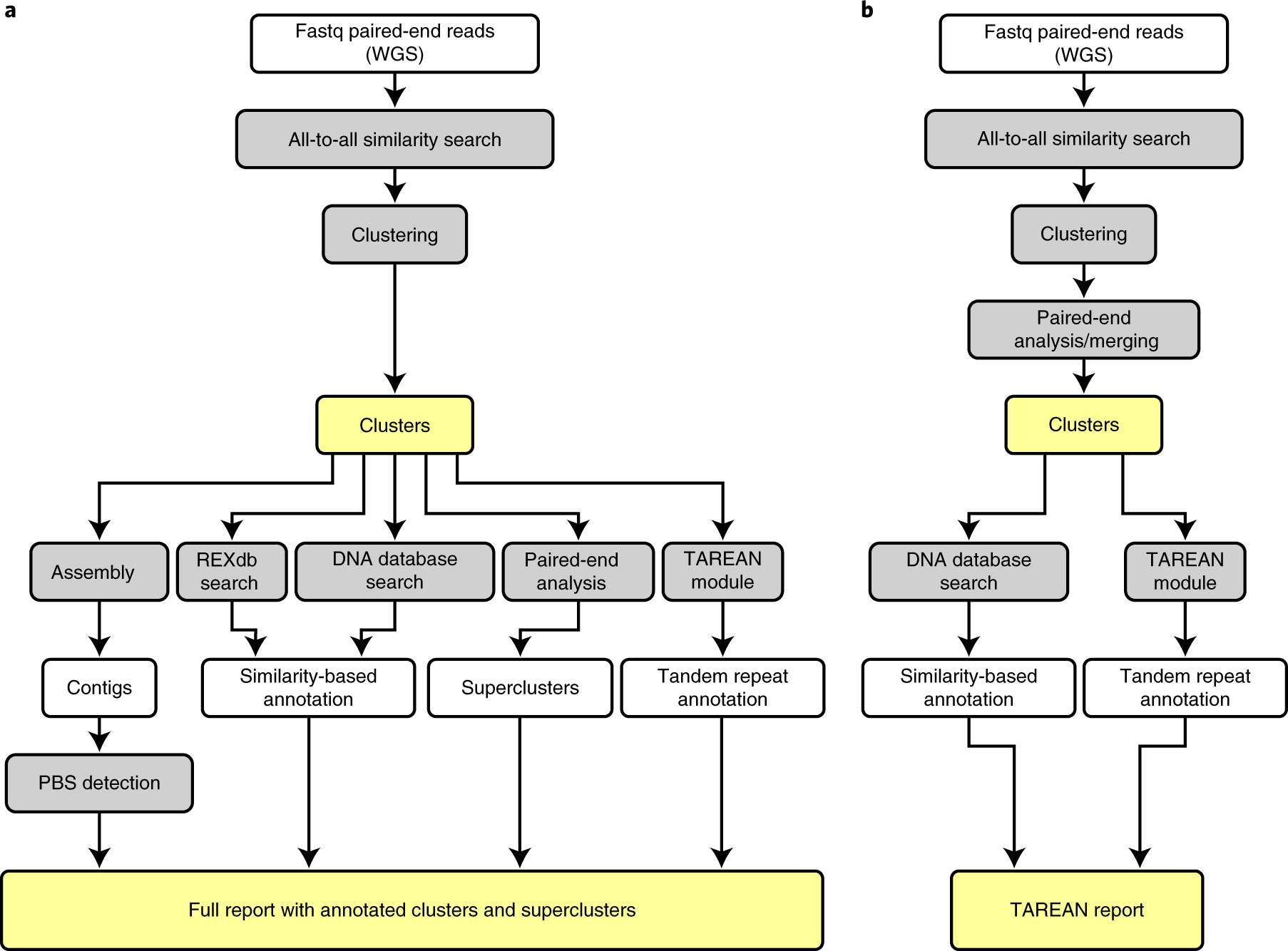



Global Analysis Of Repetitive Dna From Unassembled Sequence Reads Using Repeatexplorer2 Nature Protocols
The sequence of bases on each strand are arranged so that all of the bases on one strand pair with all of the bases on another strand, ie the number of guanosines always equals the number of cytosines and the number of adenines always equals the number of thymines RNA can fold so that base pairing occurs between complementary regionsNucleotide structure The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA)DNA and RNA are made up of monomers known as nucleotidesIndividual nucleotides condense with one another to form a nucleic acid polymerEach nucleotide is made up of three components a nitrogenous base (for which there are five different types), a pentose Q Pair up the nucleotide bases with their complementary partners Drag each Item to the appropriate bin Solved • Nucleic Acids Q Sort these nucleotide building blocks by their name or classification What is the complementary DNA sequence to 5′ ATGCATCG 3′?




Molecular Biology Of The Cell 5th Edition Silo Pub




Freight Operations Geodis
• Label a base pair • Label the sugarphosphate backbones • Label the hydrogen bonds!!Part A Pair up the nucleotide bases with their complementary partners Drag each item to the appropriate bin Hint 1 The difference between purines and pyrimidines The complementary partners in a DNA base pair are always made up of one purine and one pyrimidine, never two purines or two pyrimidinesA Complementary basepairing allows replication to begin at one end of the molecule and proceed to the other B During replication, two entirely new DNA molecules are produced, each a complement of the other C



Apcentral Collegeboard Org Pdf Ap Biology Teacher Lab Manual Effective Fall 19 Pdf



2




Calameo Fdl Proceedings Public



1



Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Complementary Chegg Com




Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Chemistry And Life Pdf Functional Group Base Pair




Sarcopenia Aging Related Loss Of Muscle Mass And Function Abstract Europe Pmc



Http Www Nsfc Gov Cn English Site 1 Pdf Nsfc annual report 19 Pdf




Dna And Rna Part 2 Base Pair Dna




Crystal Structures Of The Pilus Retraction Motor Pilt Suggest Large Domain Movements And Subunit Cooperation Drive Motility Abstract Europe Pmc



Print Exam 3 Chs 5 Dna Structure And Replication Machinery 16 The Molecular Basis Of Inheritance Flashcards Easy Notecards



Mcb Hw Pics Notes Studocu




Mb Ch 5 Pt 2 Adaptive Follow Up Set 3 Flashcards Quizlet




Nutrients December 19 Browse Articles




Ucsc Genome Browser News Archives




Scientifically Apps Free Course By Dawson Education Services Co Op On Itunes U



Print Exam 3 Chs 5 Dna Structure And Replication Machinery 16 The Molecular Basis Of Inheritance Flashcards Easy Notecards



Www Nsf Gov Attachments Public 18 Mgi Pi Meeting Abstract Book Draft Pdf




5 12 Png Part A Q 12 Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Complementary Partners Drag Each Item To The Appropriate Bin View Available Hint S Reset Course Hero




5 12 Png Part A Q 12 Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Complementary Partners Drag Each Item To The Appropriate Bin View Available Hint S Reset Course Hero




The Importance Of Technology Transfer Better World



Www Geneious Com Assets Documentation Geneious Geneiousprimemanual 0 Pdf




The Ucsc Genome Browser Karolchik 12 Current Protocols In Bioinformatics Wiley Online Library



Igv User Guide




Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Co Clutch Prep




Identification Of A Novel Topoisomerase Inhibitor Effective In Cells Overexpressing Drug Efflux Transporters Topic Of Research Paper In Biological Sciences Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open



Www Geneious Com Assets Documentation Geneious Geneiousprimemanual19 0 Pdf




Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Co Clutch Prep




Mb Ch 5 Pt 2 Adaptive Follow Up Set 3 Flashcards Quizlet



21 Recently Added Removed Ebooks Libraries At Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center




5 12 Png Part A Q 12 Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Complementary Partners Drag Each Item To The Appropriate Bin View Available Hint S Reset Course Hero




Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Co Clutch Prep




Problem Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Complementary Par




Technical Program



Http Www Nsfc Gov Cn English Site 1 Pdf Nsfc annual report 19 Pdf



Extensionpublications Unl Edu Assets Pdf Mp110 Pdf



Www Cgl Ucsf Edu Chimera Pdf Usersguide1 10 Pdf




Mb Ch 5 Pt 2 Adaptive Follow Up Set 3 Flashcards Quizlet




Linux Dictionary Manualzz



1



Protocols For Molecular Dynamics Simulations Of Rna Nanostructures Springerlink



Tamu Edu Academicaffairs Media Media Apr Collegeofagricultureandlifesciences bp Self Study 21 Pdf




Us 10 543 485 B2 Slip Chip Device And Methods Rpx Insight



Capsules Ppt By Sameera



Spie Org Documents Conferencesexhibitions Dss11 abstracts Pdf




March 1 Volume Lxxxviii No 5 By Kirkus Reviews Issuu



Welch1 S3 Us West 1 Amazonaws Com Media Reports Complete Supplement 15 C Pdf Mtime




New Zealand Computer Science Research Student Conference




Pdf Plant Genetics Biotechnology And Forestry



Www Aphis Usda Gov Brs Aphisdocs 19 309 01p Pdf



Www Cbd Int Doc Meetings Abs Abswg 08 Information Abswg 08 Abswg 07 Inf 02 En Pdf



Part A Late Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Chegg Com




Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Co Clutch Prep



Era Library Ualberta Ca Items Ff F1dd 49bc 6a Dd5043afdecf Download 40d0ab67 91ca 4162 7c Ce



Http Www Seaturtle Org Mtn Pdf Mtn156 Pdf




The Ucsc Genome Browser Karolchik 12 Current Protocols In Bioinformatics Wiley Online Library




Mastering Biology Chapter 16 Rhs Homework




A Pressure Test To Make 10 Molecules In 90 Days External Evaluation Of Methods To Engineer Biology Journal Of The American Chemical Society



Www Media Discoveryeducation Com Wp Content Uploads 05 Ca Stb High Biology Labs Pdf



Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Complementary Chegg Com




Mastering Biology Chapter 16 Rhs Homework



Msacad Org Wp Content Uploads 13 04 Vol 66 July 3 Journal Of Mas Abstract Issue21 Autosaved 7 24 21 Pdf




Mastering Biology Chapter 16 Rhs Homework
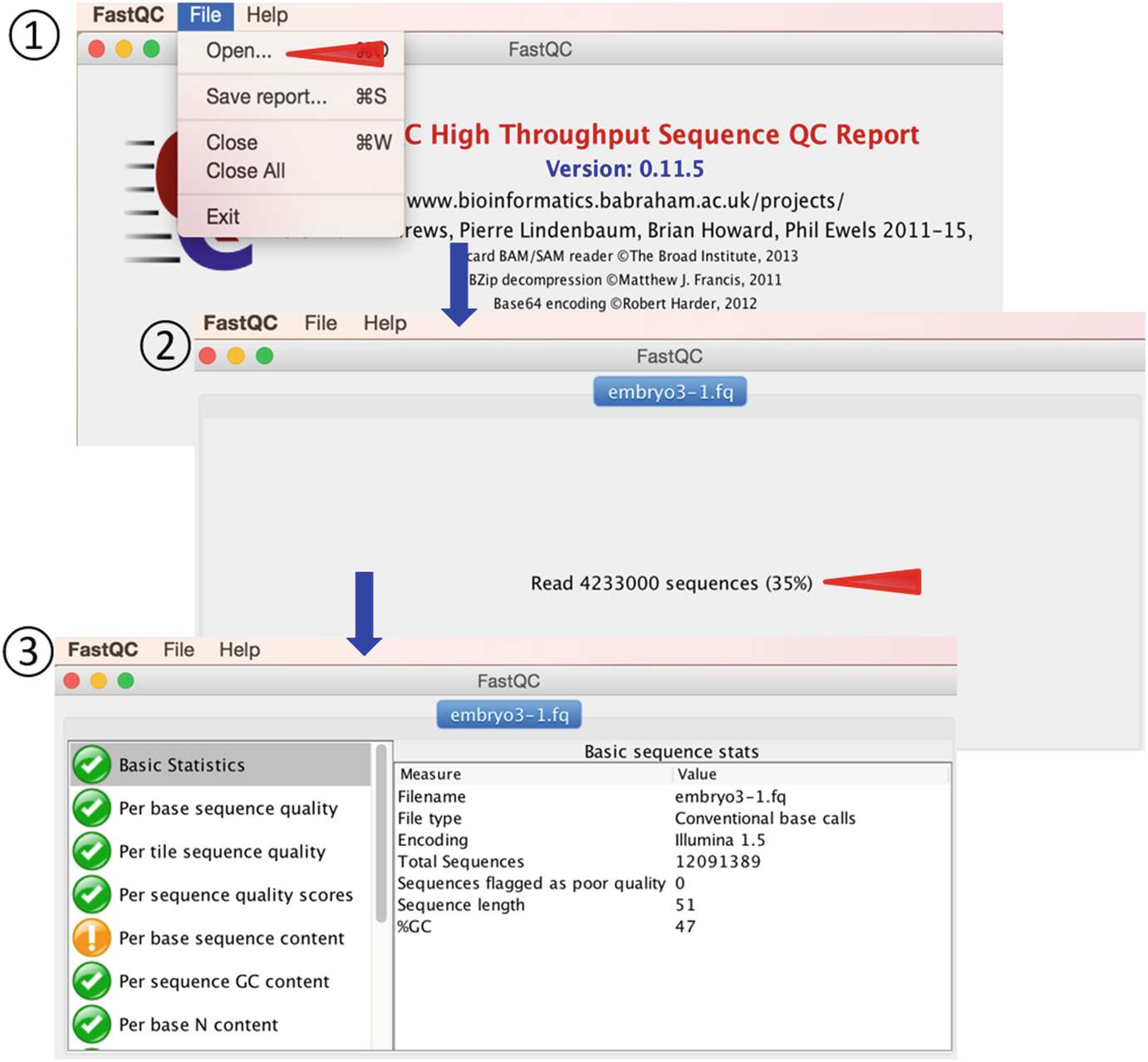



An Easy To Follow Pipeline For Long Noncoding Rna Identification A Case Study In Diploid Strawberry Fragaria Vesca Springerlink



1



Www Aps Anl Gov Files Aps Uploads Aps Science Aps Science 05 Pdf




50 Points Drag The Tiles To The Correct Boxes To Complete The Pairs Match The Nitrogenous Base Of Brainly Com




Dna And Rna Part 2 Base Pair Dna




Basic Introductions Dr M On Science Research Scientists
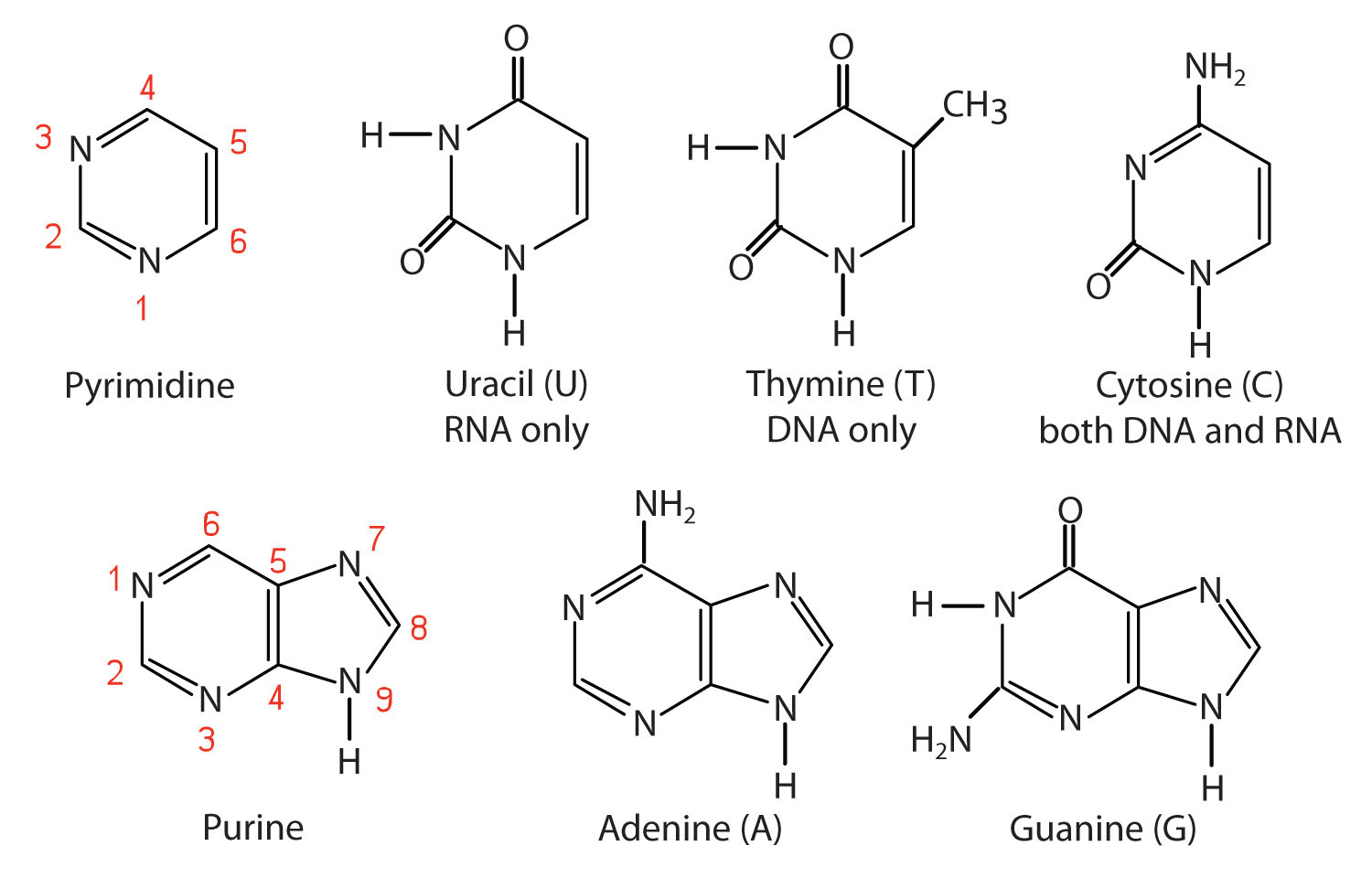



Hydrogen Bonding In Dna Base Pairs




5 12 Png Part A Q 12 Pair Up The Nucleotide Bases With Their Complementary Partners Drag Each Item To The Appropriate Bin View Available Hint S Reset Course Hero



3



Www fs Org Common Uploaded files Resources Proceedings 02 Proceedings Pdf



Pair2vec Tokens Txt At Master Mandarjoshi90 Pair2vec Github



Www Asms Org Docs Default Source Past Annual Conference Programs 57th Asms Final Program Pdf Sfvrsn Fa5d76c3 0
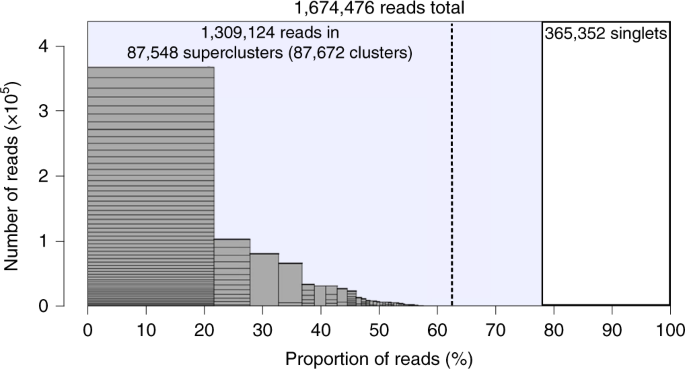



Global Analysis Of Repetitive Dna From Unassembled Sequence Reads Using Repeatexplorer2 Nature Protocols


