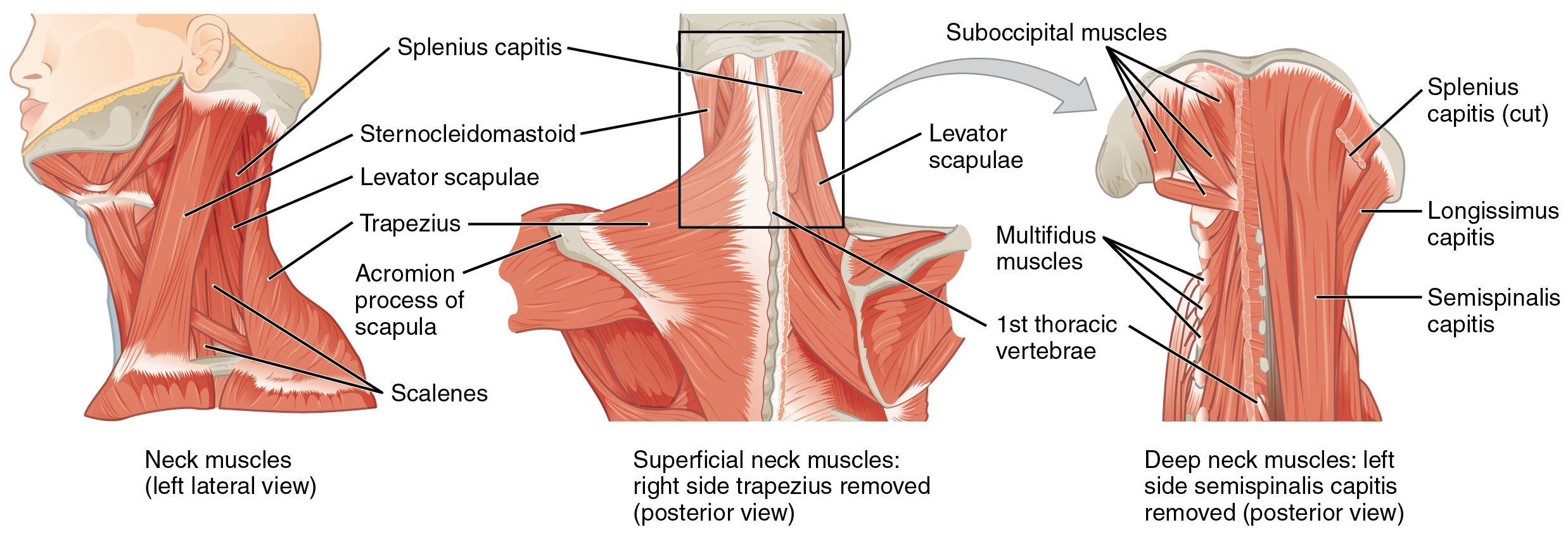
From the sides and the back of the neck, the splenius capitis inserts onto the head region, and the splenius cervicis extends onto the cervical region These muscles can extend the head, laterally flex it, and rotate it (Figure \(\PageIndex{9}\)) Figure \(\PageIndex{9}\) Muscles of the Neck and Back The large, complex muscles of the neck andThe bones of the head form a protective cavity around the brain The bones of the head meet at joint lines called sutures They are a type of fibrous joint, which are immovable The 22 bones of the skull can be divided in to two main categories the cranium and the facial skeleton From the sides and the back of the neck, the splenius capitis inserts onto the head region, and the splenius cervicis extends onto the cervical region These muscles can extend the head, laterally flex it, and rotate it (Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\)) Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\) Muscles of the Neck and Back

Massage For Neck Pain Headaches Suboccipitals
Back of head region anatomy
Back of head region anatomy- Head and neck anatomy is important when considering pathology affecting the same area In radiology, the 'head and neck' refers to all the anatomical structures in this region excluding the central nervous system, that is, the brain and spinal cord and their associated vascular structures and encasing membranes ie the meningesThe Organs of the Head include the ear, the eye, the nose and sinuses, the salivary glands, and the oral cavity The ear can be divided in to three sections the external ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear The external ear functions to capture and direct sound waves through the external acoustic meatus to reach the tympanic membrane (ear drum)




Snell S Clinical Anatomy By Regions Medicine Health Science Books Amazon Com
In other words, there is a muscle on the forehead (frontalis) and one on the back of the head (occipitalis), but there is no muscle across the top of the head Instead, the two bellies are connected by a broad tendon called the epicranial aponeurosis , or galea aponeurosis (galea = The neck refers to the collection of structures that connect the head to the torso It is a complex structure composed of many bones, muscles, nerves, blood vessels, lymphatics, and other connective tissues The cervical spine is the bony part of the neck Its primary function is to provide support for the skull, while still allowing for movement It is the most flexible part of the Head and upper neck disorders may be called craniovertebral (or craniocervical) junction abnormalities (CVJ) The CVJ is one of the unique and complex areas of your body, as this is where your brain transitions to your spine The CVJ is composed of the occipital bone, atlas (C1), and axis (C2), along with a network of complex nerve and vascular
The neck is the start of the spinal column and spinal cord The spinal column contains about two dozen interconnected, oddly shaped, bony segments, called vertebrae The neck contains seven ofThe occipital bone (/ ˌ ɒ k ˈ s ɪ p ɪ t əl /) is a cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput (back and lower part of the skull)It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish The occipital bone overlies the occipital lobes of the cerebrumAt the base of skull in the occipital bone, there is a large oval opening called the foramen magnum, which allows the The majority of blood draining from the head is passed into three pairs of veins • vertebral veins Within the brain all veins lead to the internal jugular veins The external jugular veins are smaller than the internal jugular veins and lie superficial to them They receive blood from superficial regions of the face, scalp and neck
This is a region of the neurocranial portion of the head and includes the temporal and infratemporal fossae, superior and inferior to the zygomatic arch, respectively Oral region This is a median region of the face or viscerocranial portion of the head and includes the oral cavity , teeth , gingivae , tongue, palate, and the region of the palatine tonsils Neck layers • Prevertebral Layer • Surrounds the vertebral column and its associated muscles (scalence, prevertebral, and deep muscles of the back) • In the inferior region of the neck, the fascia surrounds the brachial plexus and subclavian artery, and here it The occipital bone is the trapezoidshaped bone at the lowerback of the cranium (skull) The occipital bone houses the back part of the brain and is one of seven bones that come together to form the skull It is located next to five of the cranium bones




Skull Anatomy Terminology Dr Barry L Eppley



1
Posterior (or dorsal) means the opposite of anterior "back of" or "behind/on the back" This is easy to remember because "posterior" is another word for your rear end, which is on your backside An anatomy test question might ask, "Your sternum is _____ to your spine" The answer is that your sternum is anterior to the spineIn other words, there is a muscle on the forehead ( frontalis) and one on the back of the head ( occipitalis ), but there is no muscle across the top of the head Instead, the two bellies are connected by a broad tendon called the epicranial aponeurosis, or galea aponeurosis (galea =The Crown begins at the point where the top of the head begins to curve downward to the back of the head and ends at the point just above the Occipital bone It is a semicircular area Occipital BoneThe Occipital Bone is the small bony protrusion at




Snell S Clinical Anatomy By Regions Medicine Health Science Books Amazon Com




To Clinically Oriented Anatomy Basicmedical Key
Start studying External Anatomy of Head and Neck Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools the region of the head surrounding and including the auricle a broad back muscle that forms the uppermost border of the shoulder The mucus from the sinuses drains into your nasal passages and then down the back of your throat to be swallowed sinus anatomy like structure that runs through the abdominal regionStructure Bones The head rests on the top part of the vertebral column, with the skull joining at C1 (the first cervical vertebra known as the atlas)The skeletal section of the head and neck forms the top part of the axial skeleton and is made up of the skull, hyoid bone, auditory ossicles, and cervical spine The skull can be further subdivided into



1




Bones Of The Head Teachmeanatomy
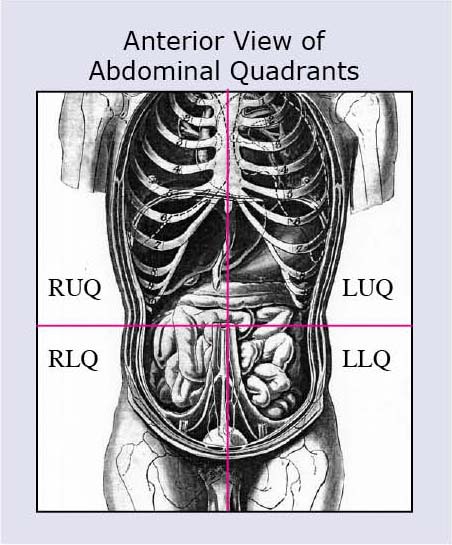
The back is the body region between the neck and the gluteal regions It comprises the vertebral column (spine) and two compartments of back muscles ;The frontal plane, also called the coronal plane, which divides the body into front and backAnatomy regions Flashcards Browse 500 sets of anatomy regions flashcards Study sets Diagrams Classes Users 13 Terms Darla_Crompton Regional Anatomy (Abdominopelvic Regions) Right Upper Quadrant (RUQ) 1/4 Left Upper Quadrant (LUQ) 2/4 Right Lower Quadrant (RLQ) 3/4



Skull Anatomy Pictures And Information
/male-skull-in-profile-with-transparent-head-on-white-background-1092338382-d031fe3a88fa4462b0ba082a1ec64302.jpg)



Occipital Bone Anatomy Function And Treatment
Extrinsic and intrinsic The back functions are many, such as to house and protect the spinal cord , hold the body and head upright, and adjust the movements of the upper and lower limbsAncient Greek and Latin words are used to build anatomical terms A standard reference position for mapping the body's structures is the normal anatomical position Regions of the body are identified using terms such as "occipital" that are more precise than common words and phrases such as "the back of the head" In addition to housing main parts of the nervous system — the brain and spine — and the start of the digestive system, the head contains many important sensory organs




Occipital Neuralgia And Suboccipital Headache C2 Neuralgia Treatments Without Nerve Block Or Surgery Caring Medical Florida
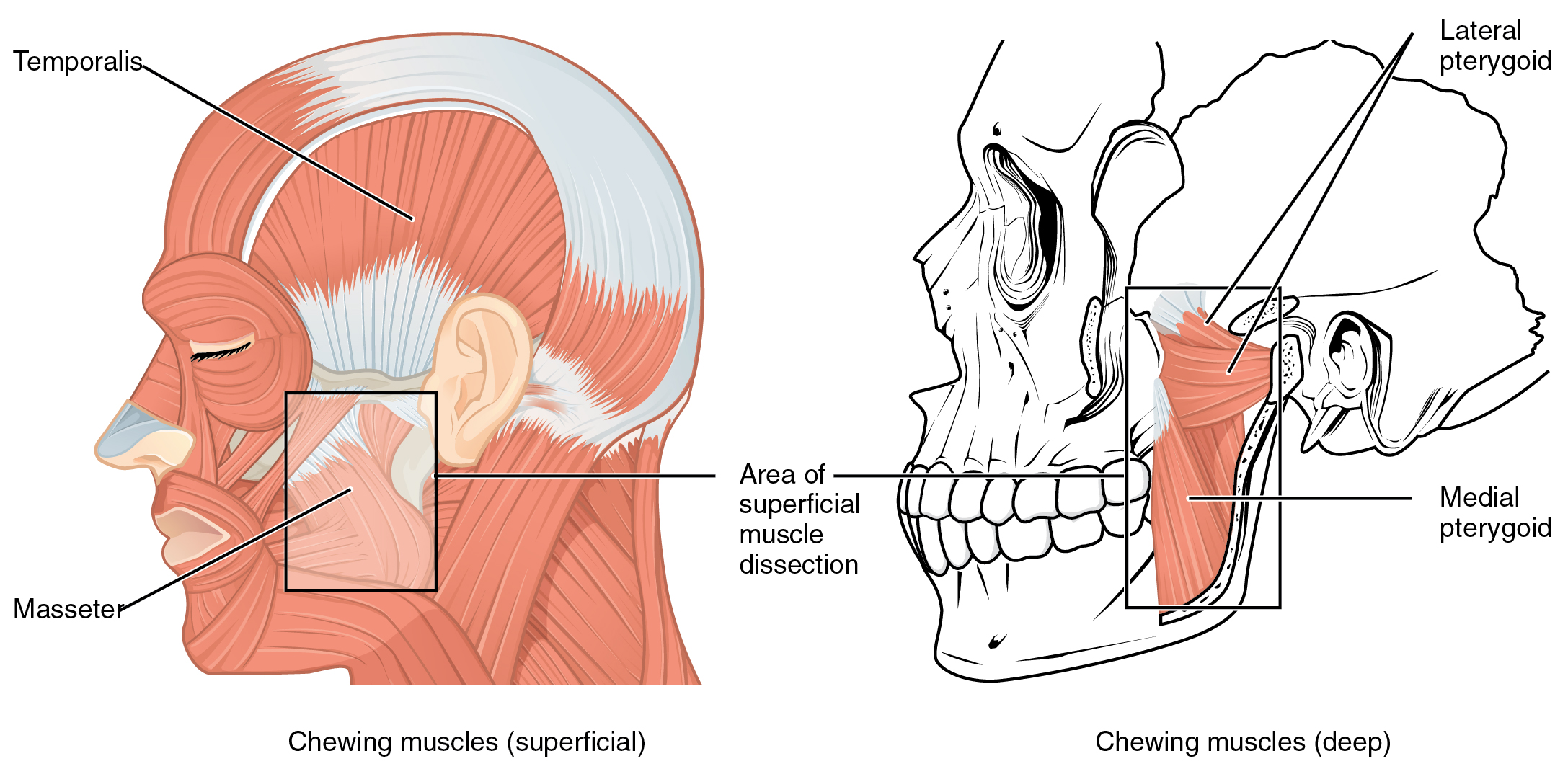



Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And Physiology
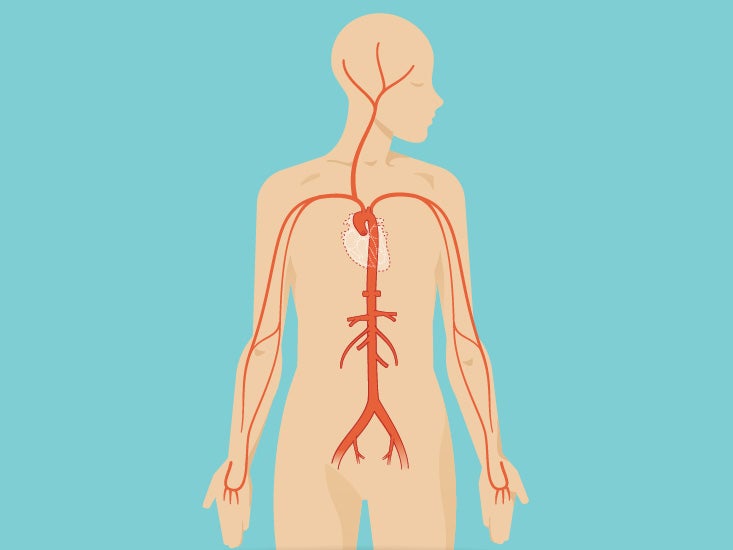
The anatomical regions (shown) compartmentalize the human body Just like on a map, a region refers to a certain area The body is divided into two major portions axial and appendicular The axial body runs right down the center (axis) and consists of everything except the limbs, meaning the head, neck, thorax (chest and back), The head and neck receives the majority of its blood supply through the carotid and vertebral arteries This article shall explore the anatomy of this arterial system – its anatomical course, branches, and clinical correlationsC2 and C3 Posterior head and neck • T4 Nipple • T10 – Umbilicus Natural Variants The dermatome is a basic concept, yet much variability exists between dermatome maps in standard anatomy and medical guideline textbooks A review of 14 different dermatome maps by Lee et al showed striking variations within each individual map 7




Cervical Spine Anatomy Neck




11 4 Identify The Skeletal Muscles And Give Their Origins Insertions Actions And Innervations Anatomy Physiology
The muscles of the back categorize into three groups The intrinsic or deep muscles are those muscles that fuse with the vertebral column The second group is the superficial muscles, which help with shoulder and neck movements The final group is the intermediate muscles, which help with the movement of the thoracic cage Only the intrinsic muscles are considered true backThe muscle has a frontal belly and an occipital (near the occipital bone on the posterior part of the skull) belly In other words, there is a muscle on the forehead ( frontalis) and one on the back of the head ( occipitalis ), but there is no muscle across the top of the headThe back has different muscle groups that work together to allow movement There are groups of muscles that move the Head Shoulders Upper arms Spine (vertebral column) Upper leg (thigh) Other muscles beyond the back also help move the head, shoulders, arms, and legs For example, some muscles located in the chest also help move the shoulders



Lab 1 Anatomical Terminology Summer Crn Biol110m Section A Anatomy Physiology I
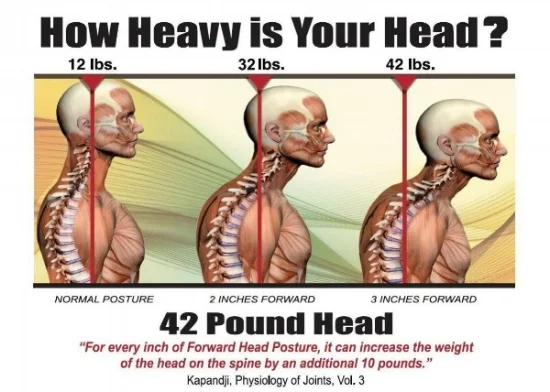



The Link Between Posture And Chronic Neck And Upper Back Pain Back Pain And Headache Specialist Burke Va Nova Headache Chiropractic Center
Infraorbital Region The infraorbital region of head is situated below the orbital region and corresponds to the upper part of the anterior surface of the maxilla The infraorbital foramen lies in this region about 1 cm below the infraorbital margin consistent together with the supraorbital notch or foramen The knowledge of its location is essential for providing infraorbital In the neck and head exterior to the skull, the external carotid artery provides blood flow to the skin, muscles, and organs Several major arteries including the facial, superficial temporal, and occipital arteries branch off from the external carotid to provide blood to the many superficial structures of the headFemale Head Muscles Anatomy Back Clip Art by Decade3D 5 / 142 the head muscles Clipart by Eraxion 5 / 50 Female Head Muscles Anatomy Back Stock Illustration by Decade3D 4 / 500 Male backbone with skull posterior view Stock Illustrations by woodoo 3 / 244 Thoracic spine anatomy posterior view Clip Art by woodoo 3 / 176 Blood supply of the brain, eps10 Stock Illustrations by




Massage For Neck Pain Headaches Suboccipitals
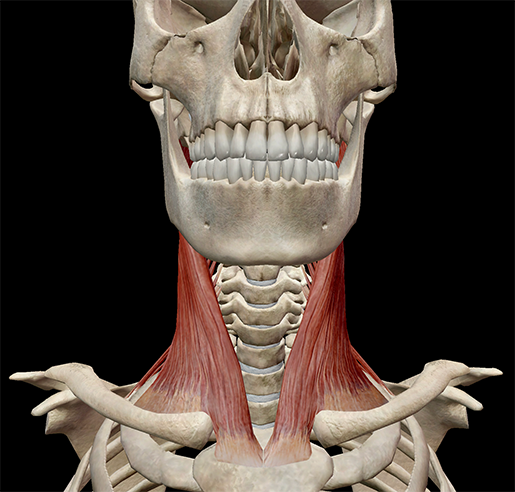



Learn Muscle Anatomy Scalene Muscles And Other Neck Anatomy
An overview of the descriptive regions of the head The names of the regions often relate to the structures of those regions, and it can help to have an idea Venous Drainage The venous drainage of the scalp can be divided into superficial and deep components The superficial drainage follows the arterial supply superficial temporal, occipital, posterior auricular, supraorbital and supratrochlear veins The deep (temporal) region of the skull is drained by the pterygoid venous plexusThis is a large plexus of veins situatedAnatomical terms describe structures with relation to four main anatomical planes The median plane, which divides the body into left and right This passes through the head, spinal cord, navel, and, in many animals, the tail;




Occipital Neuralgia Causes Symptoms Diagnosis And Treatment




11 4 Identify The Skeletal Muscles And Give Their Origins Insertions Actions And Innervations Anatomy Physiology
Deep back muscles The deep back muscles, also called intrinsic or true back muscles, consist of four layers of muscles superficial, intermediate, deep and deepest layersThese muscles lie on each side of the vertebral column, deep to the thoracolumbar fascia They span the entire length of the vertebral column, extending from the cranium to the pelvisThe occipital glands (lymphoglandulæ occipitales), one to three in nu ber, are placed on the back of the head close to the margin of the Trapezius and resting on the insertion of the Semispinalis capitisTheir afferent vessels drain the occipital region of the scalp, while their efferents pass to the superior deep cervical glands The posterior auricular glands (lymphoglandulæ auricularesThis course takes the learner back to the basics of oral anatomy As time moves away from those first few terms of college, we often forget the names, location, and functions of the space we spend so much time in, the head and neck region This course is designed to help oral health clinicians review anatomical structures of the head and neck




Skull Anatomy Terminology Dr Barry L Eppley




Temporal Bone Anatomical Diagram Function And Injuries
Studying the neck anatomy will sometimes provide real clues as to the true nature of chronic neck pain, so it is always advised for any neck ache sufferer to fully comprehend their diagnostic conclusion, including the affected anatomical structures in their cervical spineThe neck features a complex anatomy, with the frontal region being filled with vital structures, such as the Human head (anterior view) The human head is more than just a nuisance responsible for your headaches It is a complex anatomical structure weighing up to five kilograms that rests on the bony skull and in turn, the neckIn addition to the evident ears, eyes, nose, and mouth, the head supports a variety of other important structures Muscles of masticationAreas of the Head 8 Topics Bones of the Head 7 Topics Muscles of the Head 3 Topics Nerves of the Head 5 Topics Organs of the Head




Standard Anatomical Position An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Skull Scalp And Superficial Face
Projection of a meningea media (Krönlein) r frontalis r parietalis Linea horizontalis auriculoorbitalis Linea horizontalis supraorbitalis Linea verticalis zygomaticaThe sagittal planes, which are parallel to the median plane; CHAPTER 25 Head and neck overview and surface anatomy This chapter contains an overview of the topographical anatomy of the head and neck described in detail in Chapters 26–34 Chapter 27 Chapter 28 Chapter 29 Chapter 30 Chapter 31 Chapter 32 Chapter 33 Chapter 34, and an account of the clinically relevant surface anatomy




Upper Cervical Spine Disorders Anatomy Of The Head And Upper Neck



Anatomical Terms Meaning Anatomy Regions Planes Areas Directions
There are seven cervical vertebrae that allow for a great amount of motion in the neck When looking from behind, in most individuals, the spine looks straight However, when viewing the spine from the side, there are distinct curves to each part of the spine




How Does Occipital Nerve Stimulation Work




Occipital Neuralgia And Suboccipital Headache C2 Neuralgia Treatments Without Nerve Block Or Surgery Caring Medical Florida



Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And Physiology




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader




Muscles Advanced Anatomy 2nd Ed




What Is Surface Anatomy Mvm Group Of Institutions



Neck Anatomy Area Diagram Body Maps
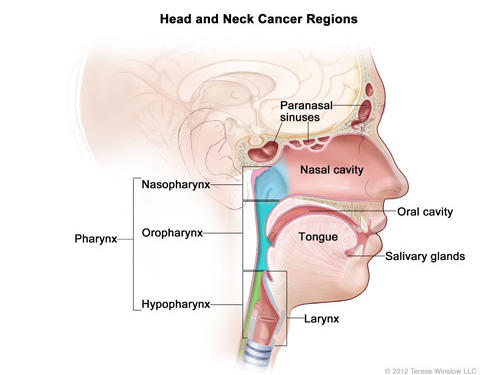



Head And Neck Cancers National Cancer Institute
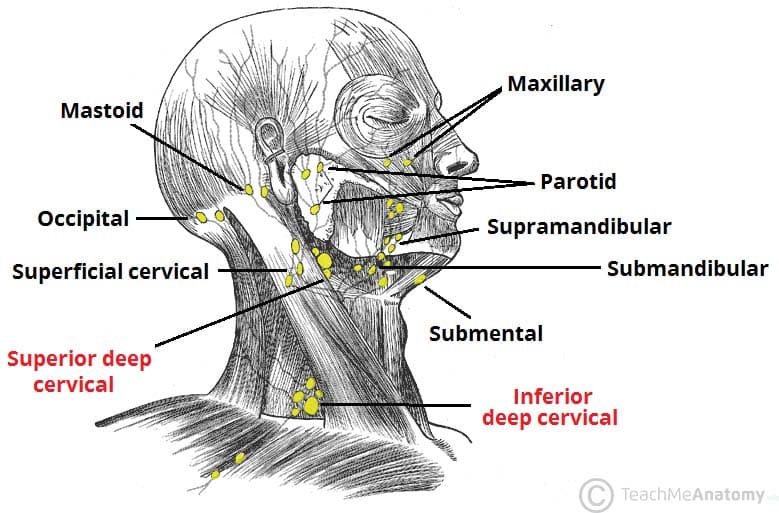



Lymphatic Drainage Of The Head And Neck Teachmeanatomy



1



The Link Between Posture And Chronic Neck And Upper Back Pain Back Pain And Headache Specialist Burke Va Nova Headache Chiropractic Center




Overview Of The Head And Neck Region Knowledge Amboss




Anatomy Cephalic Region Head Diagram Quizlet
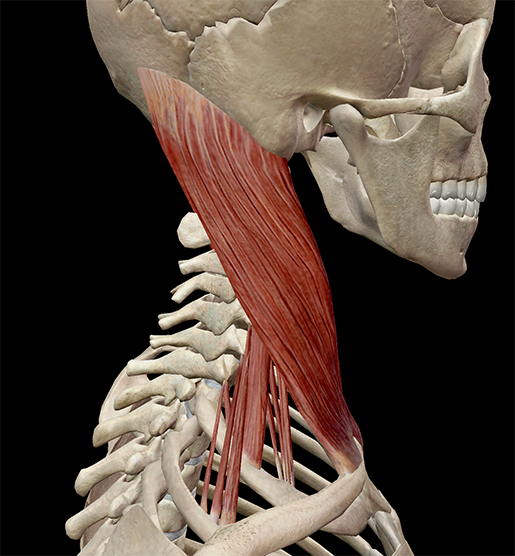



Learn Muscle Anatomy Scalene Muscles And Other Neck Anatomy



Head 3d Interactive Anatomy Tutorials




10 29 Lecture 16 Pt 2 Head And Neck Skull Face Skull Face Muscles Muscles And Triangles Of The Neck Flashcards Quizlet
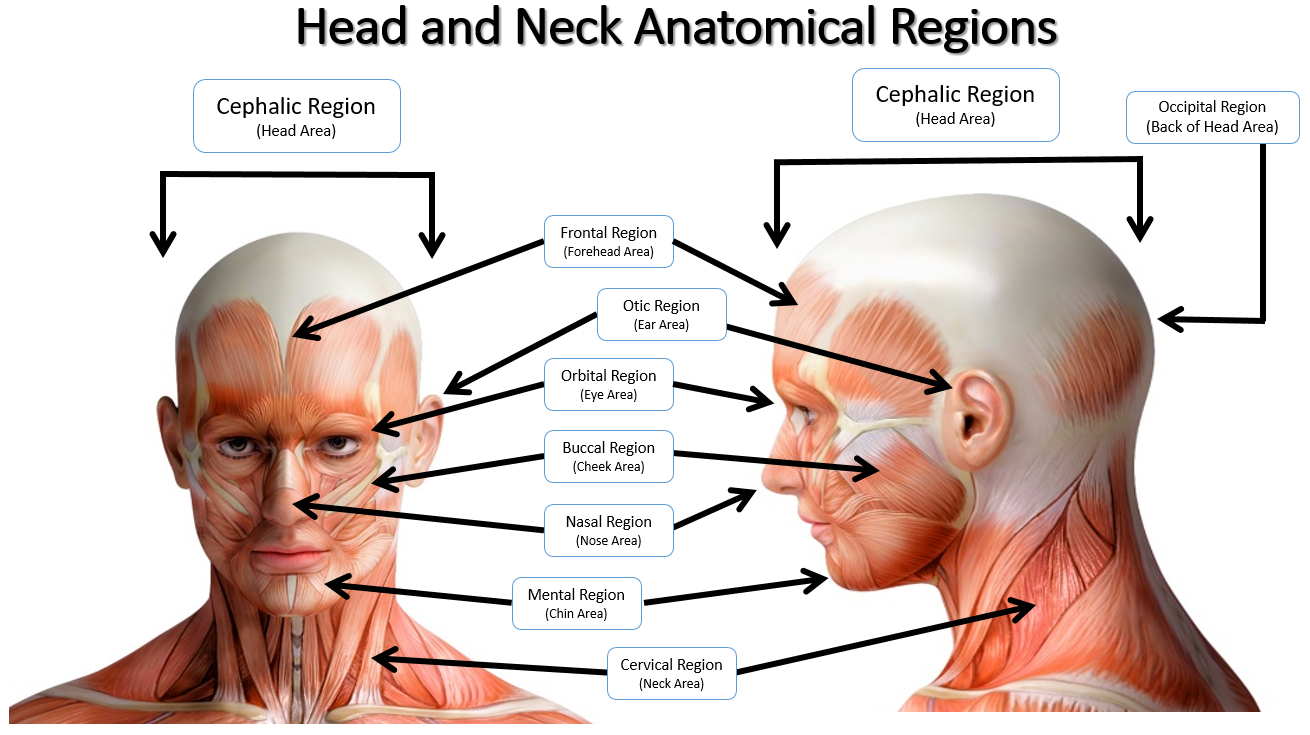



Anatomical Regions Scientist Cindy
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/10668/main-bones-of-skull_english__1_.jpg)



Head And Neck Anatomy Structures Arteries And Nerves Kenhub
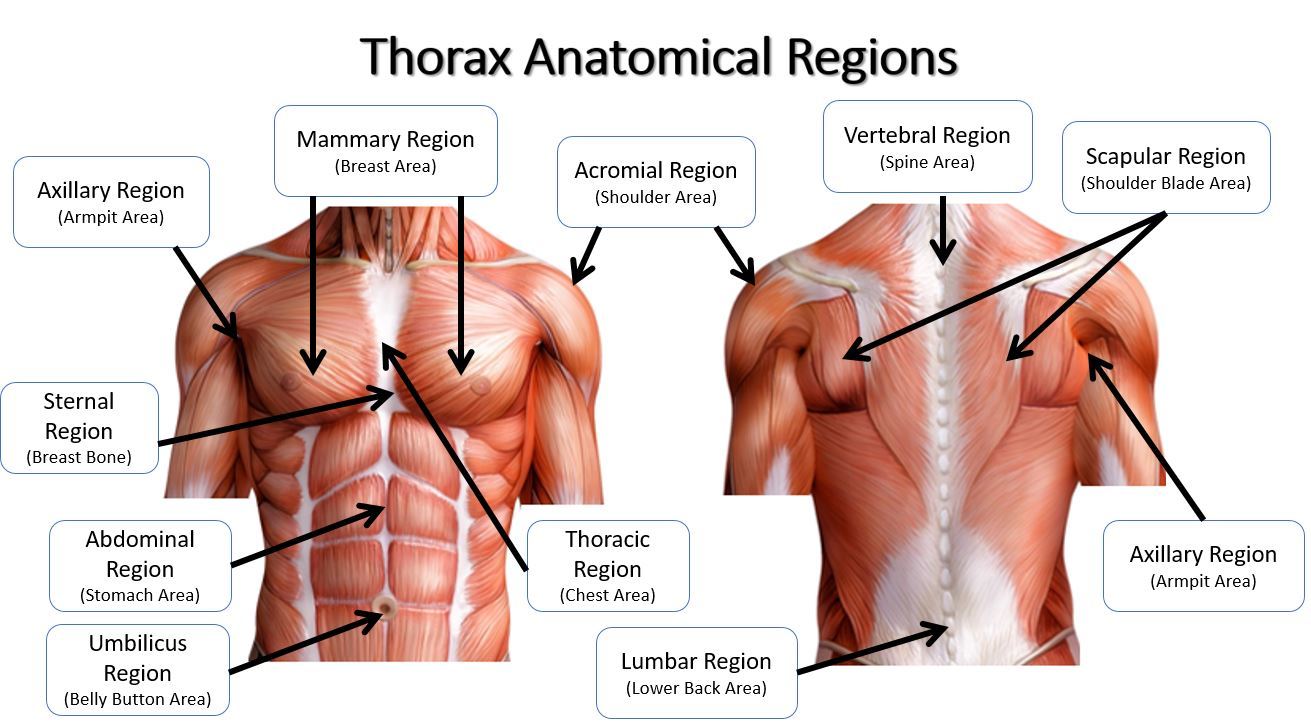



Anatomical Regions Scientist Cindy




List Of Human Anatomical Regions Wikipedia
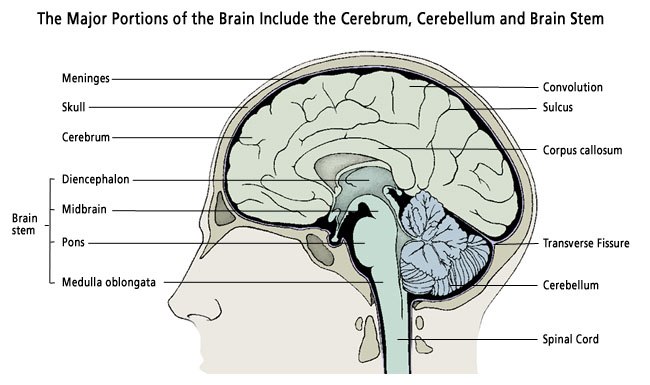



Brain Anatomy Princeton Brain Spine And Sports Medicine
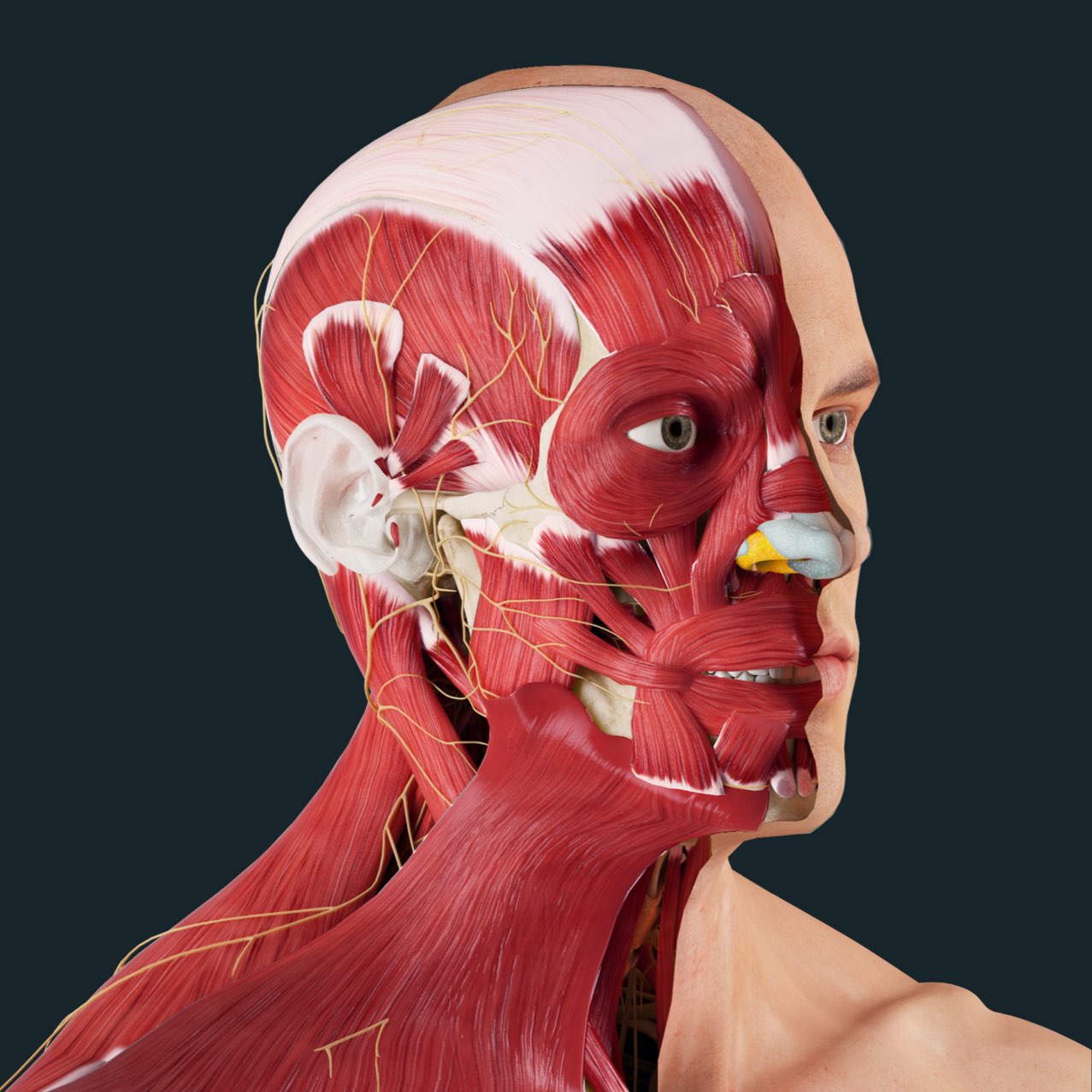



Gross Head And Neck Anatomy




Label The Body Regions Biology Libretexts




Good Morning Anatomy N N Anatatemnein Cut Apart



Muscle Anatomy



3
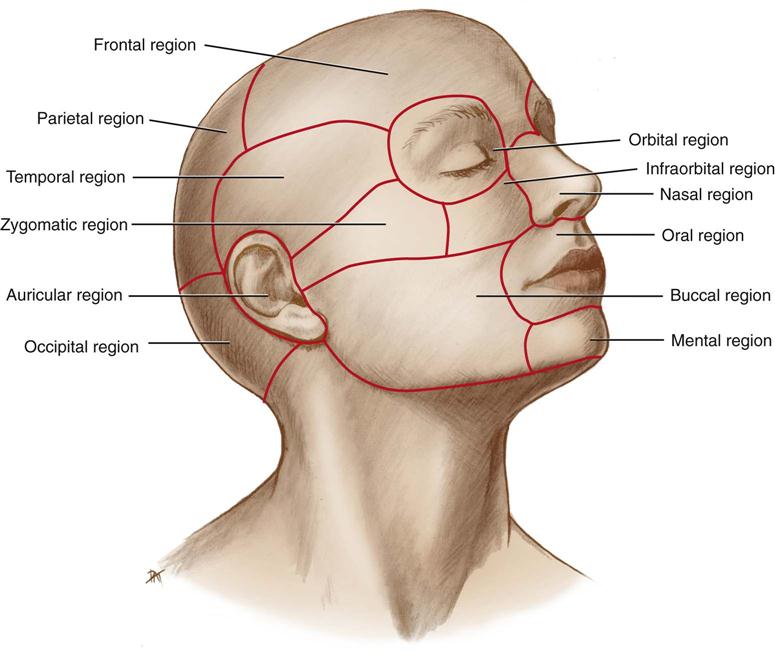



Ch 9 Head Neck Anatomy Lessons Blendspace




Primary Neck Cancer Anatomy




Temple Anatomy Wikipedia




Cranial Bones Function And Anatomy Diagram Conditions Health Tips



Lamission Edu




Anatomical Regions Youtube




A Ak Treatment With The Anatomical Device At The Back Of The Hand Download Scientific Diagram




The Muscles Of The Head And Neck Human Anatomy And Physiology Lab Bsb 141




Head Definition Anatomy Britannica
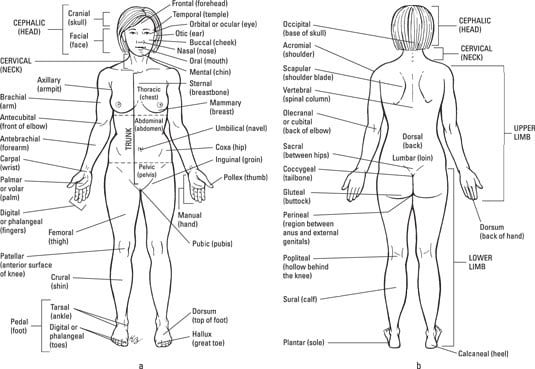



The Anatomical Regions Of The Body Dummies




List Of Human Anatomical Regions Wikipedia




Language Of Anatomy Human Anatomy And Physiology Medical Terminology Study Human Body Anatomy




Buy Head And Neck Anatomy A Clinical Reference Book Online At Low Prices In India Head And Neck Anatomy A Clinical Reference Reviews Ratings Amazon In
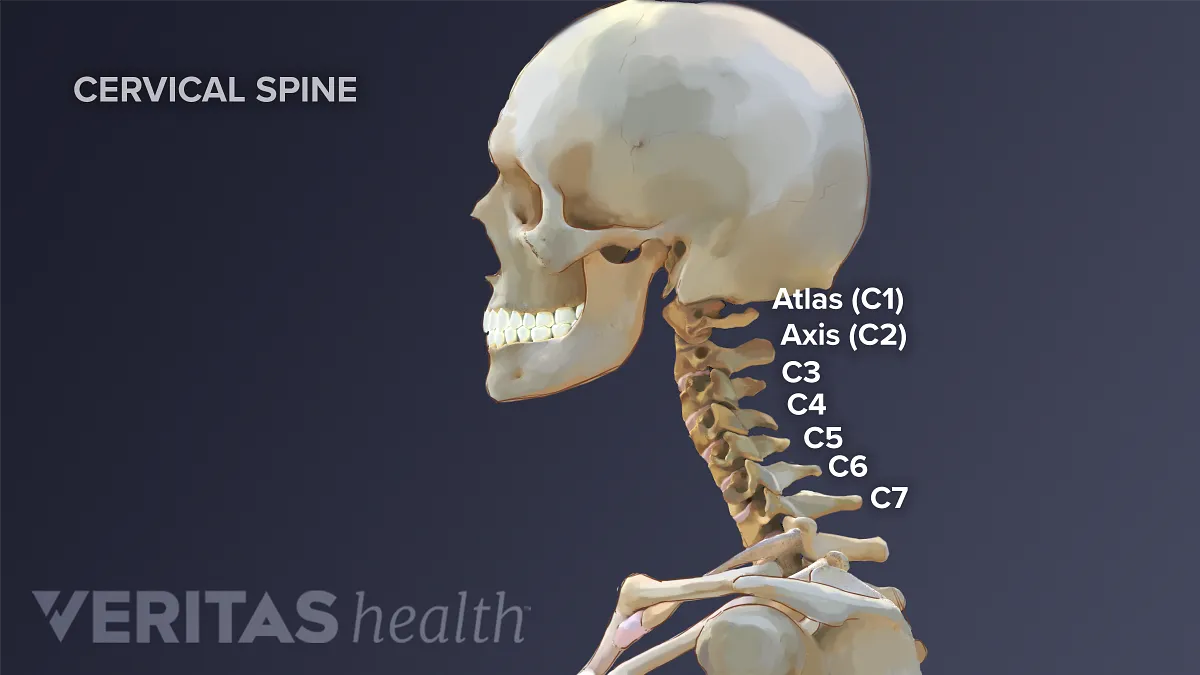



Cervical Spine Anatomy
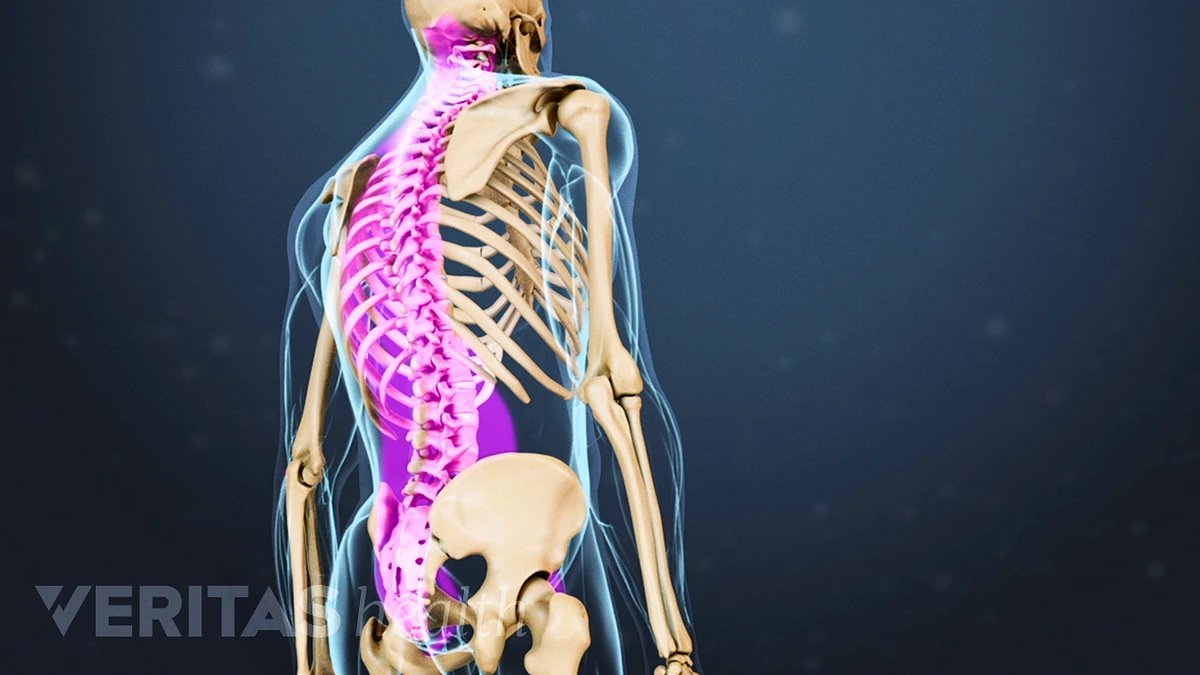



Spinal Anatomy And Back Pain
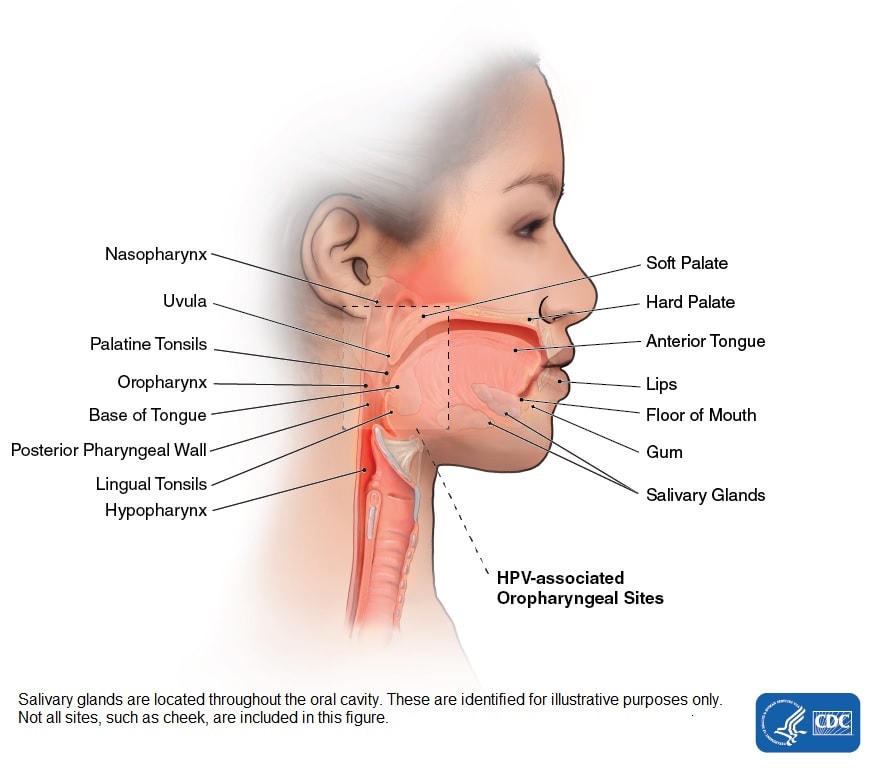



Head And Neck Cancers Cdc
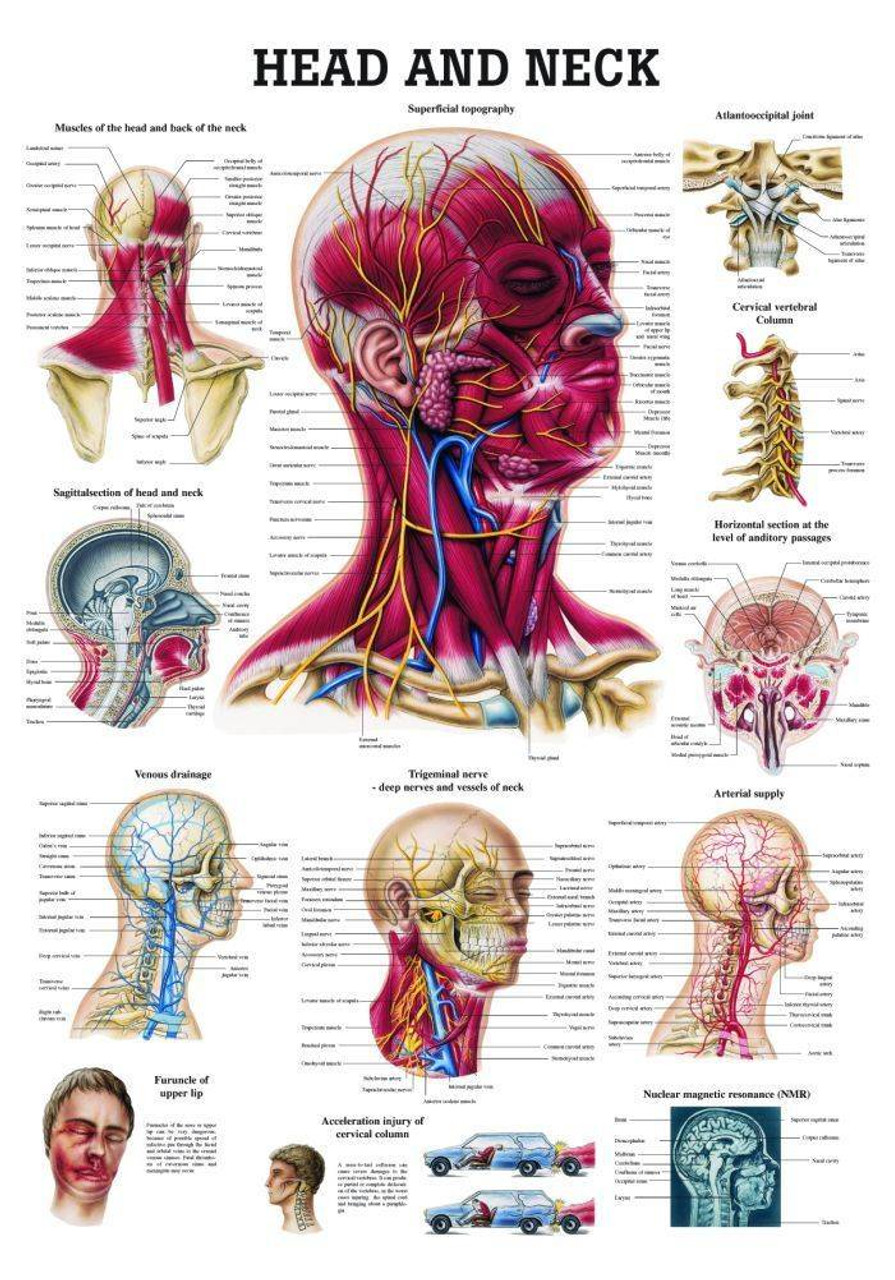



Head And Neck Laminated Anatomy Chart



Solved Bio 290 Week 1 Anatomical Directional Terms Worksheet Course Hero




Neck Anatomy Britannica
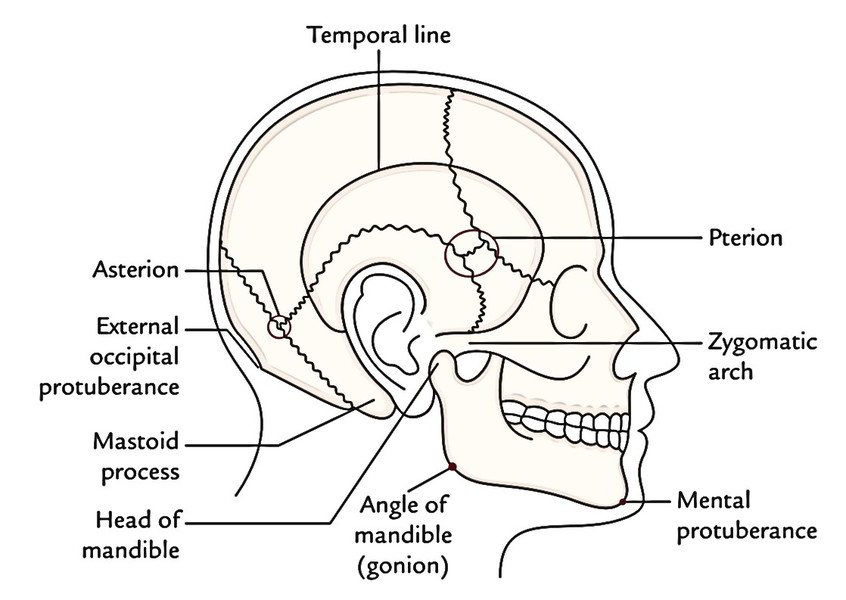



Easy Notes On Head Learn In Just 4 Minutes Earth S Lab



Muscles Of The Lumbar Spine Of The Trunk




Overview Of The Head And Neck Region Knowledge Amboss




Head And Neck Anatomy




Skull Anatomy Terminology Dr Barry L Eppley




The Human Body An Orientation Ppt Download
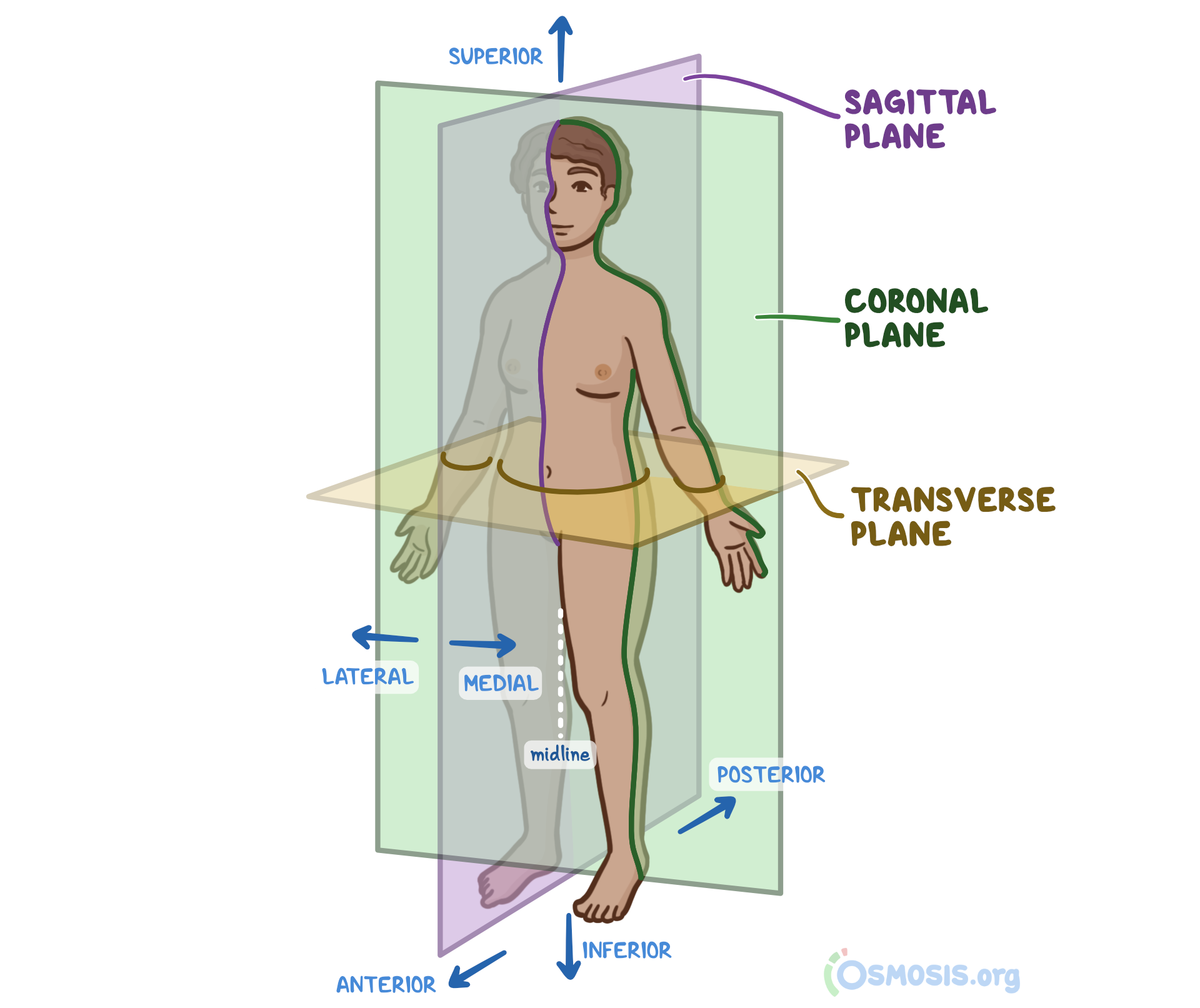



Anatomical Position What Is It Significance Regions Planes And More Osmosis




Muscles Advanced Anatomy 2nd Ed
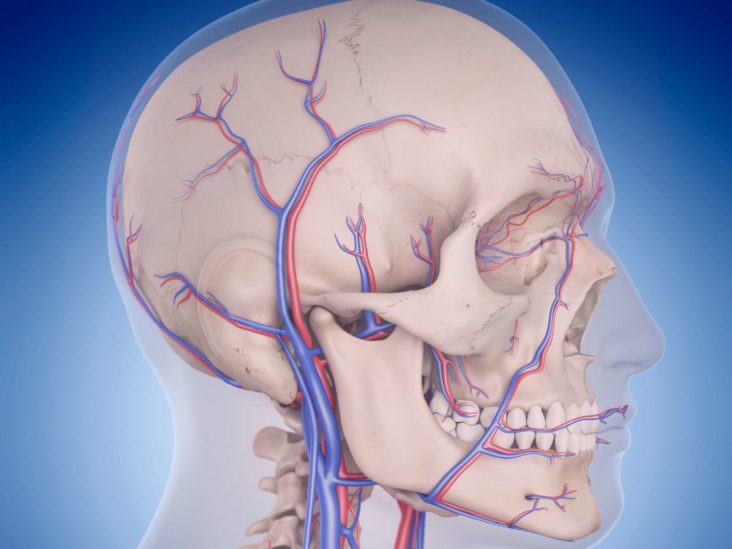



Vertebrobasilar Circulatory Disorders Symptoms And Causes




Skull Bones Mnemonic Cranial And Facial Bones Anatomy And Physiology Youtube
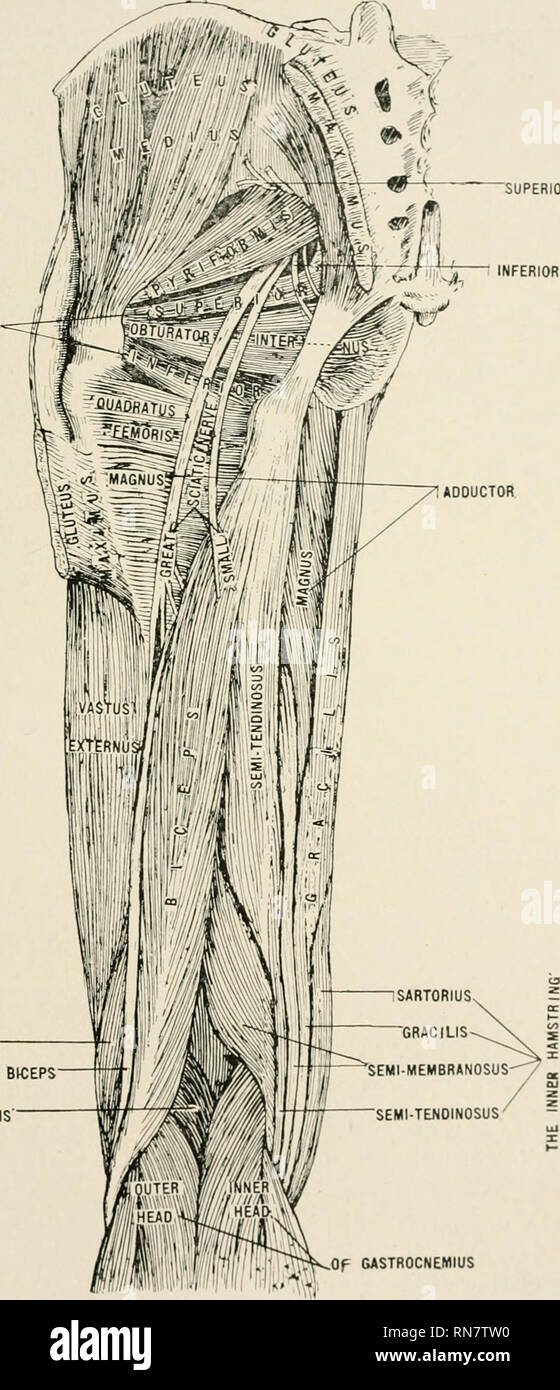



Anatomy In A Nutshell A Treatise On Human Anatomy In Its Relation To Osteopathy Human Anatomy Osteopathic Medicine Osteopathic Medicine Anatomy Plate Lxy Gemeuijs Iffj 4 Inferi0r Gloreal Crureus Short
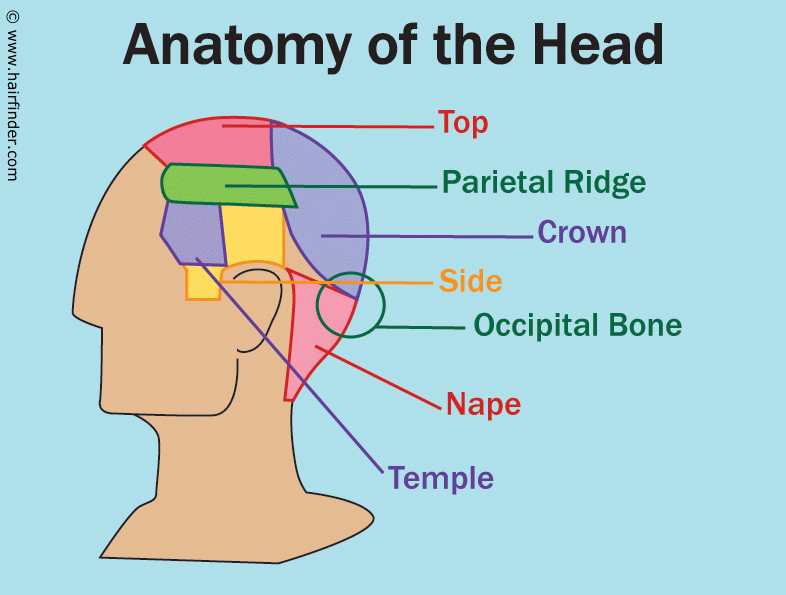



Anatomy Of The Head And The References Used For The Areas Of The Head In Haircuts And Haircutting
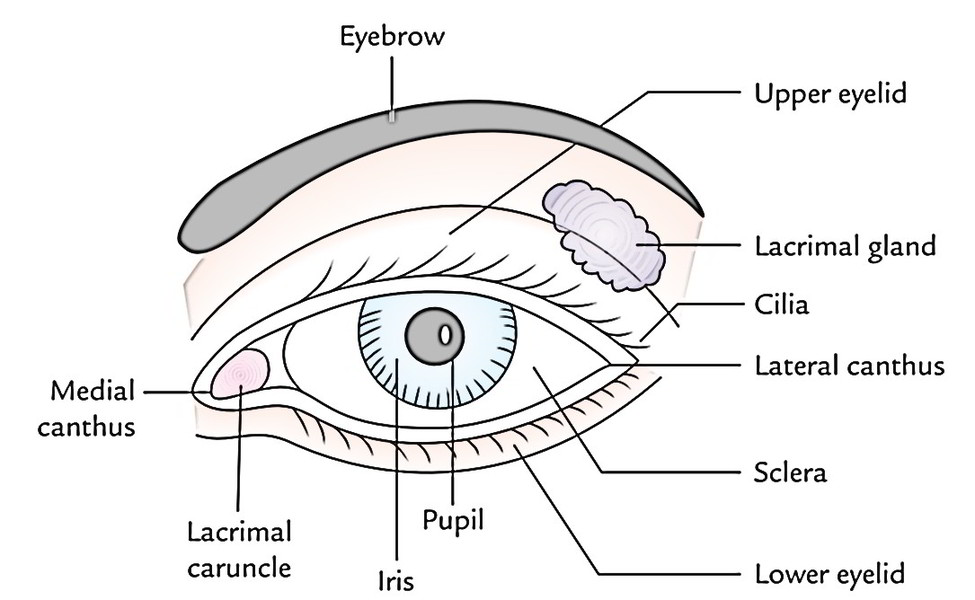



Easy Notes On Head Learn In Just 4 Minutes Earth S Lab
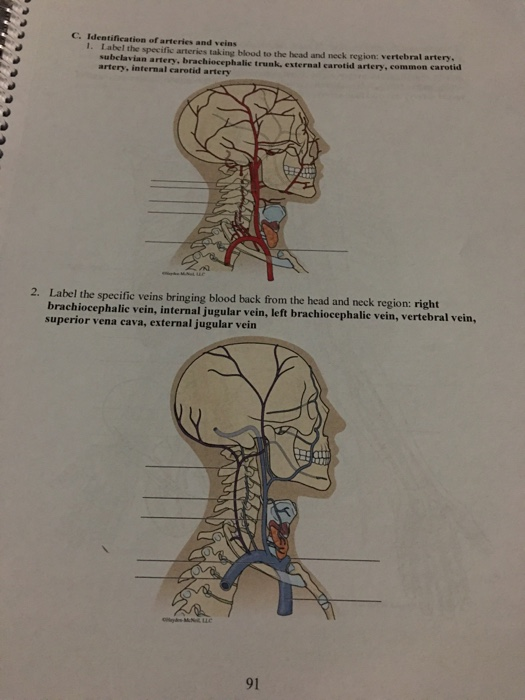



Solved C Identification Of Arteries And Veins 1 Tabel The Chegg Com




The Skull Anatomy And Physiology I



Spine Structure Function Parts Segments Spine Problems Spine Health




Olecranal Anatomy Anatomy Drawing Diagram



Ddtwo Org
/human-skull-with-veins-and-arteries--rear-view--1174640349-490cb7f8593945c4b1690b152e6a4074.jpg)



Occipital Artery Anatomy Function And Significance
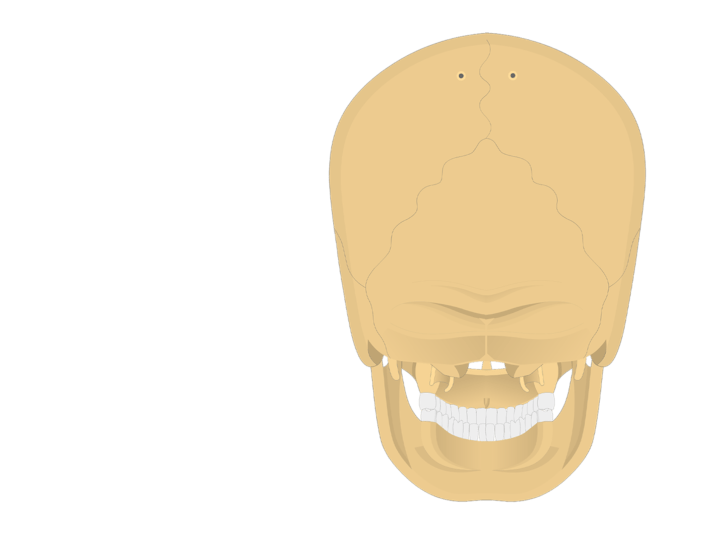



Occipital Bone Anatomy
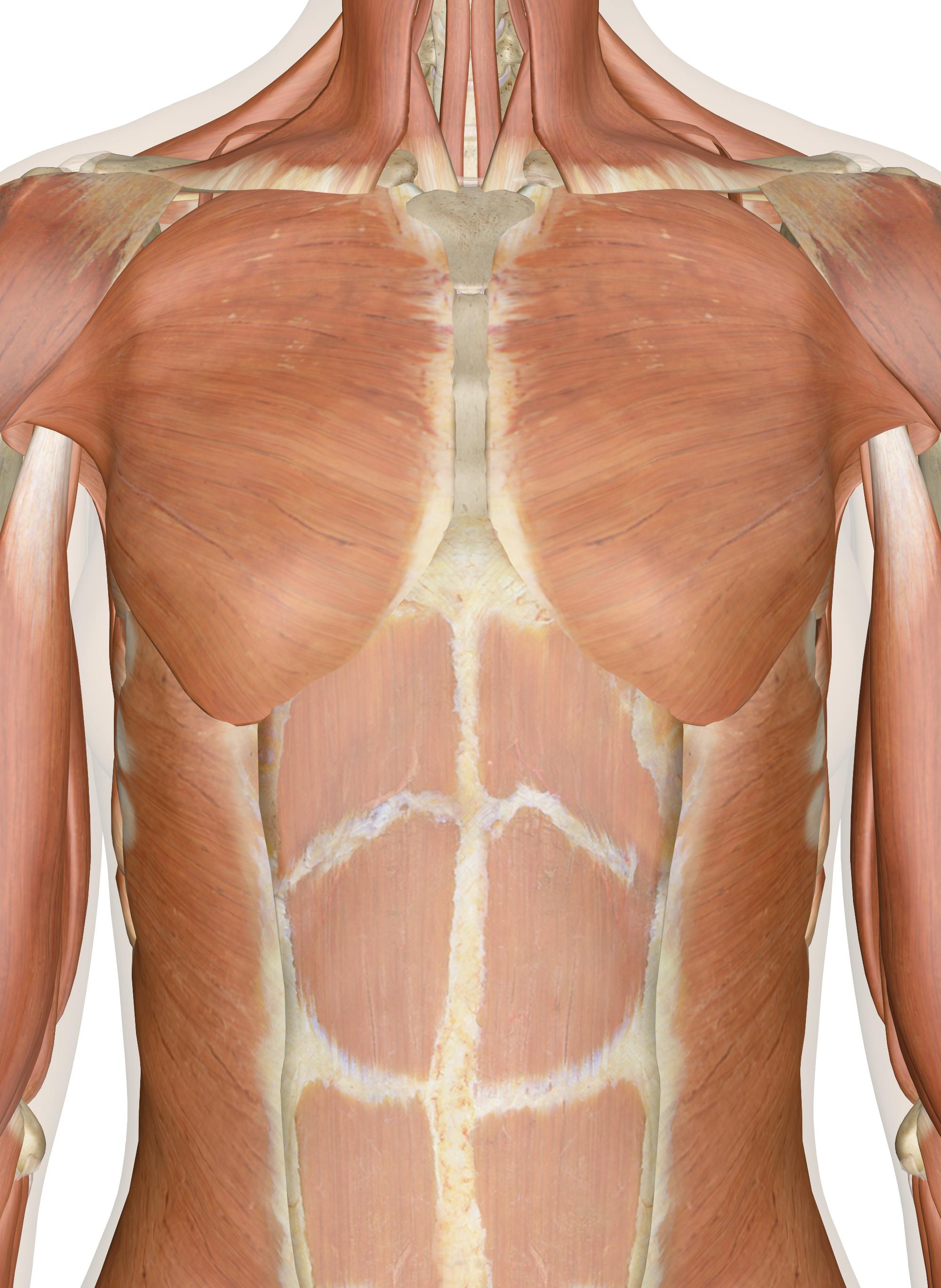



Muscles Of The Chest And Upper Back
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/7844/anterior_triangle.png)



Head And Neck Regions And Anatomy Kenhub




Overview Of The Head And Neck Region Knowledge Amboss




Muscles Of The Neck And Torso Classic Human Anatomy In Motion The Artist S Guide To The Dynamics Of Figure Drawing




Skull Scalp And Superficial Face




Back Surface Anatomy 4 Edition




Occipital Bone The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary




There Are 15 Dynamic Or Active Muscles In The Shoulder Region They Can Be Further Divided Into 3 Subc Shoulder Muscle Anatomy Shoulder Anatomy Muscle Diagram
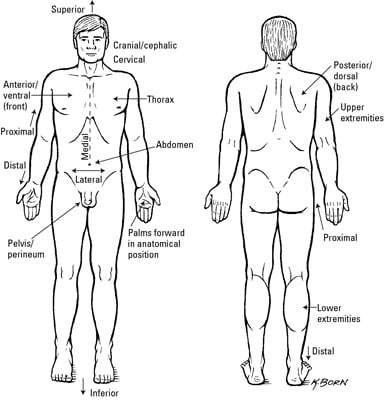



Clinical Anatomy Terms To Describe The Eight Body Regions Dummies
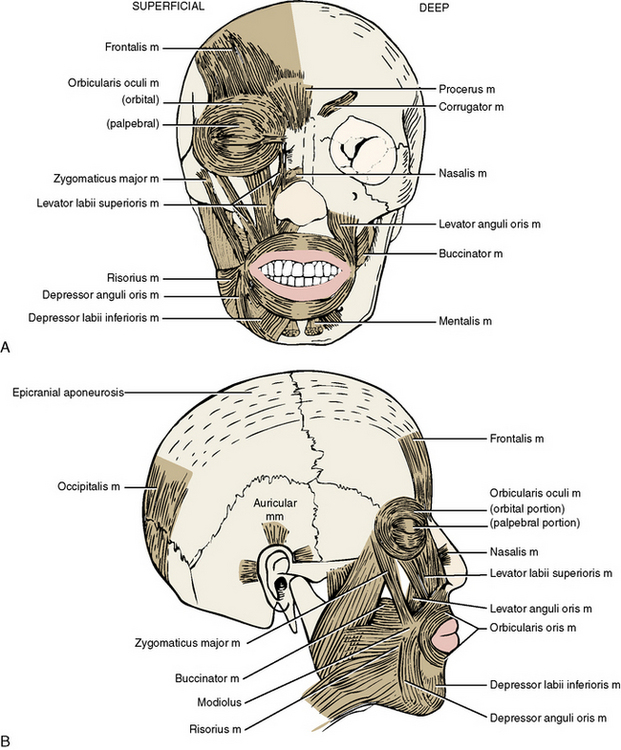



7 The Head By Regions Pocket Dentistry
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/9490/skull-posterior-lateral-views_english.jpg)



Posterior And Lateral Views Of The Skull Anatomy Kenhub
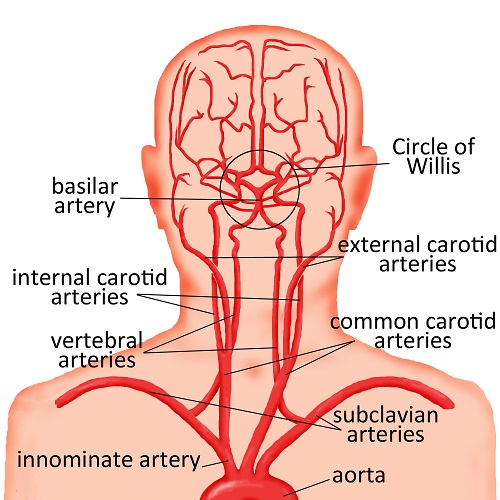



Abnormalities Of The Head And Neck Arteries Cerebrovascular Abnormalities Children S Wisconsin




Whiplash Front To Back Closed Head Injury Stock Photo Alamy
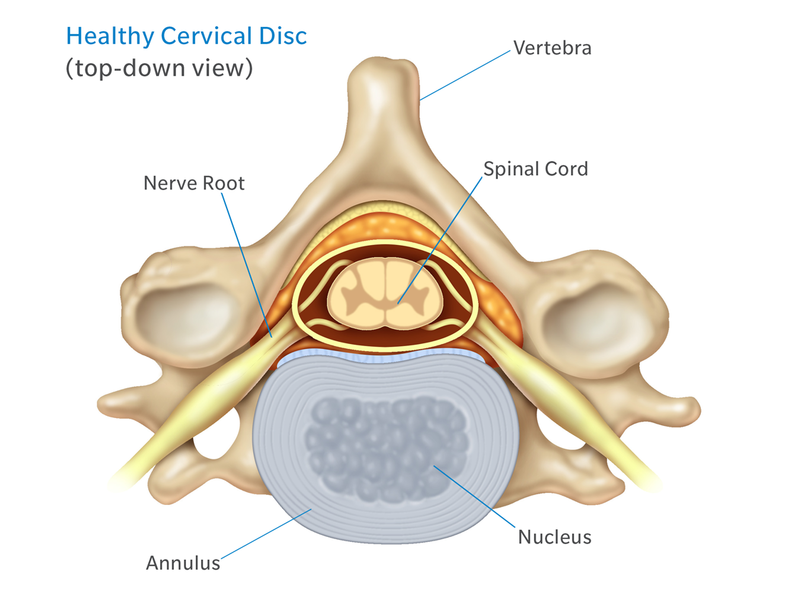



Anatomy Of The Neck Causes Of Neck Pain And How To Manage The Pain
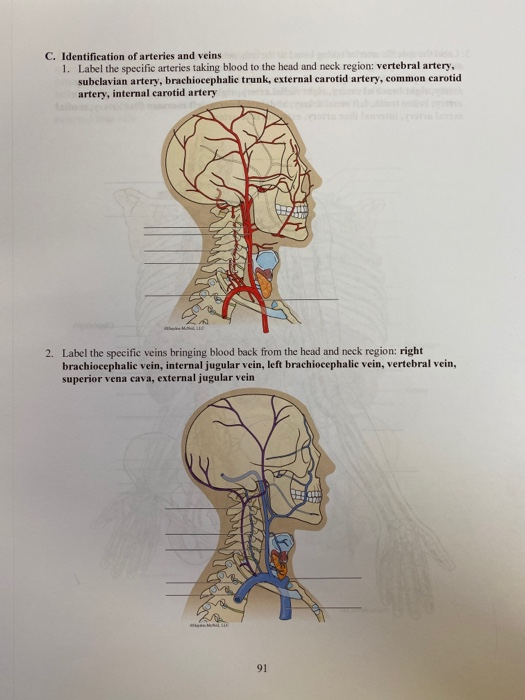



Solved C Identification Of Arteries And Veins 1 Label The Chegg Com


